Performability Evaluation of Railway Systems: A Study on the Impact of Adding Alternative Routes
Avaliação de Performabilidade de Sistemas Ferroviários: Um Estudo sobre o Impacto da Adição de Rotas Alternativas
Keywords:
Performance Evaluation, Availability, Railway SystemsAbstract
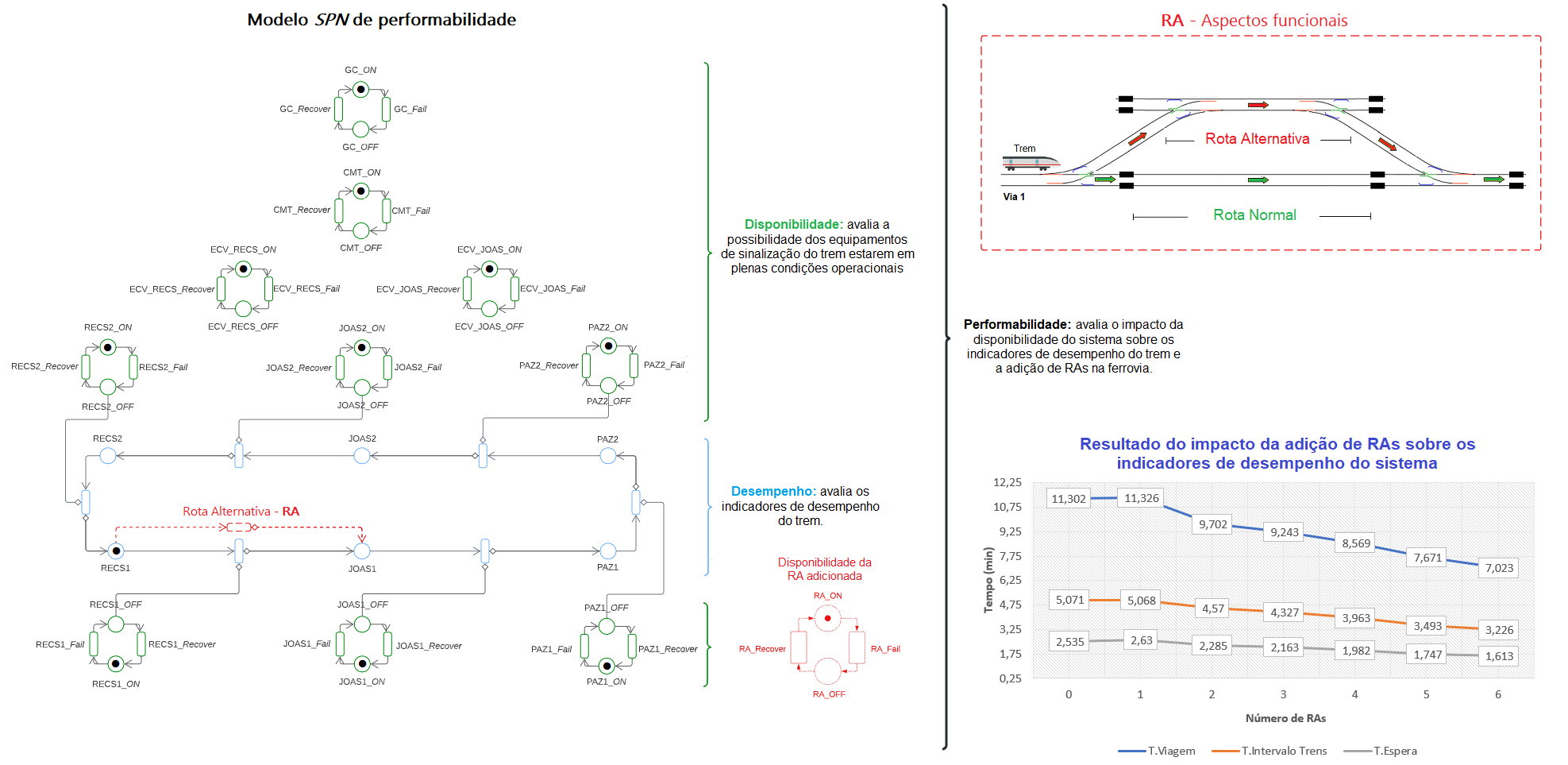
Railway systems require high performance, availability and reliability, in addition to safety and maintainability as attributes for the implementation of equipment responsible for signaling, control, and traffic of trains on the railway. Studies are necessary to deal with these essential requirements for the quality of rail systems. This article proposes a set of models in stochastic Petri nets to evaluate the impact of adding alternative routes on performance and availability indicators in railway systems. Metrics such as travel time, the interval between trains, and passenger waiting time at stations were collected and analyzed to estimate the impact of such metrics on railway systems. This work also presents case studies that simulate the implications of the availability of signaling and train control equipment on the performance of a railway and demonstrate the versatility of the proposed model in allowing the insertion of stations and varying the number of trains in the studied railway network. The results obtained demonstrate that the availability of the studied system can be increased from 81,674% to 98,456%.
Downloads
References
M. Silveira, “A importância geoeconômica das estradas de ferro no brasil.,”
in Tese (Doutorado) — Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP),
p. 4, 2003.
C. Metrorec, “Sistemas CBTU.” https://www.cbtu.gov.br/index.php/pt/
sistemas-cbtu/recife, 2021. [Online; accessed 22-Agosto-2021].
Alstom, Alstom - Railway Signaling Systems. Superintendência de
Trens Urbanos do Recife - STUREC. Gerencia de Sistemas Fixos e
Via Permanente - GOSIP., 2007.
P. Maciel, R. Lins, and P. Cunha, “Escola de computação, campinas,”
in Introdução às Redes de Petri e Aplicações, p. 4, Julho 1996.
D. Simchi-Levi and M. A. Trick, “Introduction to little’s law as viewed
on its 50th anniversary,” in Operations Research., vol. 5, p. 223, 2013.
A. Zimmermann and G. Hommel, “A train control system case study
in model-based real time system design,” in Proceedings International
Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, pp. 8 pp.–, 2003.
F. Wang and Z. Bai, “Research for urban rail transit train regulation
based on time petri nets,” in 2010 International Conference on Computer
and Communication Technologies in Agriculture Engineering, vol. 2,
pp. 461–465, 2010.
N. Hai, C.-Z. Zhang, Y. Yu, and Y. Tang, “Reliability analysis of clock
source of railway time synchronization network based on spn,” in 2019
International Conference on Intelligent Transportation, Big Data Smart
City (ICITBS), pp. 45–48, 2019.
N. Songwiroj, W. Vatanawood, and S. Vanit-Anunchai, “Railway
network modeling using building block of timed coloured petri nets,” in
IEEE 4th International Conference on Computer and Communications
(ICCC), pp. 528–533, 2018.
M. Saideh, Y. Alsaba, I. Dayoub, and M. Berbineau, “Performance
evaluation of multi-carrier modulation techniques in high speed railway
environment with impulsive noise,” in 2019 IEEE 2nd 5G World Forum
(5GWF), pp. 243–248, 2019.
D. Wu and J. Liu, “An approach to safety analysis of train control systems
with coloured petri nets,” in 2021 40th Chinese Control Conference
(CCC), pp. 4744–4750, 2021.
D. Wu, D. Lu, and T. Tang, “Qualitative and quantitative safety
evaluation of train control systems (ctcs) with stochastic colored petri
nets,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, pp. 1–
, 2021.
A. Lopes, “Universidade federal rural de pernambuco,” in Metodologia
de Análise de Desempenho de Sistemas de Transporte Público, (Recife),
pp. 18–20, 2019.
G. Callou, P. Maciel, E. Tavares, E. Andrade, B. Nogueira, C. Araújo,
and P. Cunha, “Energy consumption and execution time estimation
of embedded system applications,” Microprocessors and Microsystems,
vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 426–440, 2011.
M. S. Obaidat and N. A. Boudriga, “Fundamentals of performance
evaluation of computer and telecommunication systems.,” in John Wiley
and Sons, pp. 47–49, 2010.
W. de Souza Leonardo and G. Callou, “Stars: um ambiente integrado
para avaliação de disponibilidade, custo e consumo de energia de
sistemas,” Revista Brasileira de Computação Aplicada, vol. 13, pp. 10–
, set. 2021.
B. Silva, R. Matos, G. Callou, J. Figueiredo, D. Oliveira, J. Ferreira,
J. Dantas, A. Lobo, V. Alves, and P. Maciel, “Mercury: An integrated
environment for performance and dependability evaluation of general
systems,” in Proceedings of industrial track at 45th dependable systems
and networks conference, DSN, 2015.