Assessment of an emotions’ induction technique using stimuli from interactive digital products
Keywords:
Physiological Sensors, User Experience Evaluation, Emotional Induction Process, Human-Computer InteractionAbstract
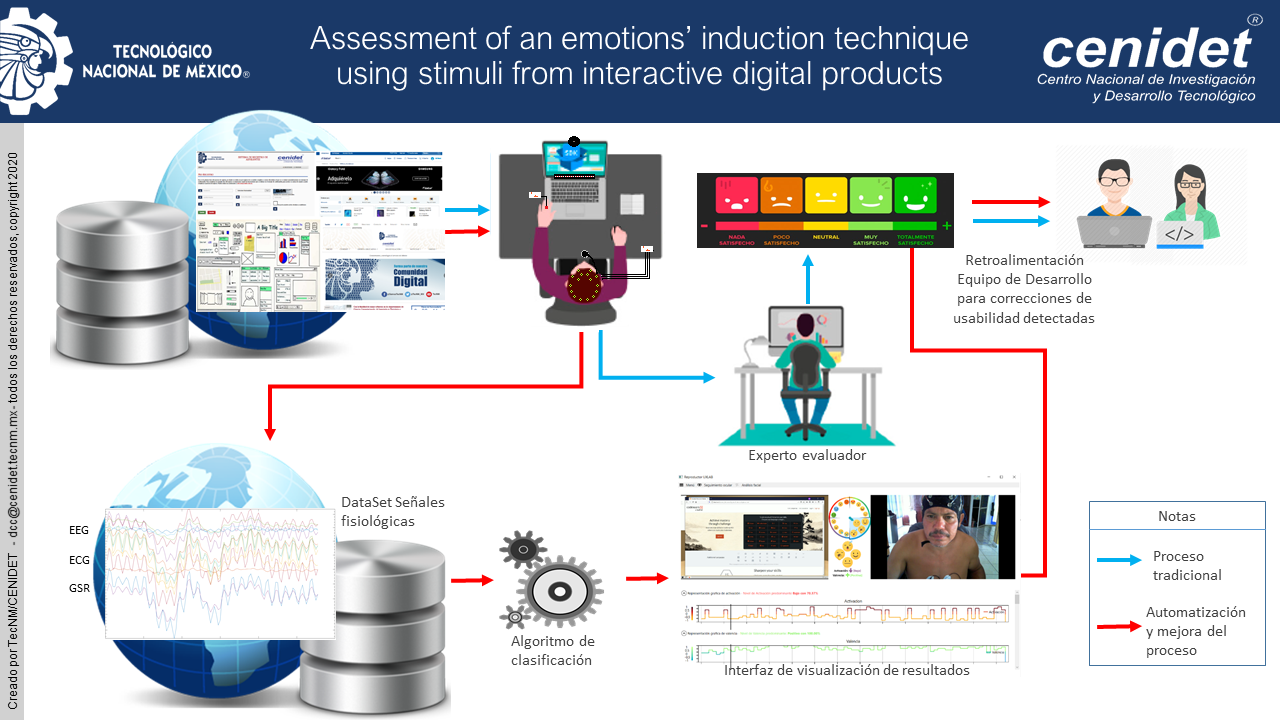
In this work we propose a new and innovative process for the induction of emotional states, through visual stimulus based on interactive user interfaces (UI), to create a dataset of emotional physiological signals that can be used in the evaluation of the user experience (UX). Most existing datasets of emotional physiological signals, were generated based on images and videos, which are not useful for analysis of emotions in the evaluation process of the user experience, for this reason in this research, we propose a new emotional induction process that allows the creation of a physiological emotion dataset focused on the evaluation process of user experience. The population sample used for the generated emotional induction process is 15 users, 7 women and 8 men, which culminated in the creation of a dataset of 333 physiological signal files plus data from the SAM questionnaires and knowing the user. The information from these questionnaires was used to perform the statistical analysis of the data, which helped to determine the relationship that exists between the study variables.
Some of the future activities planned are to increase the sample size of the datase, increase the repository of stimuli for digital products, etc.
Downloads
References
[X. P. B. Valencia, “The Possibilities of Classification of Emotional
States Based on User Behavioral Characteristics,” International Journal
of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 4–
, 2021.
L. Yang and J. Liu, “EEG-based emotion recognition using temporal
convolutional network,” Proceedings of 2019 IEEE 8th Data Driven
Control and Learning Systems Conference, DDCLS 2019, pp. 437–442,
Escalas Emociones.pdf. PhD thesis.
M. G. Huddar, S. S. Sannakki, and V. S. Rajpurohit, “Attention-based
multi-modal sentiment analysis and emotion detection in conversation
using rnn,” International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial
Intelligence, vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 112–121, 2021.
H. Chao, L. Dong, Y. Liu, and B. Lu, “Emotion recognition from
multiband eeg signals using capsnet,” Sensors (Switzerland), vol. 19,
no. 9, 2019.
S. Katsigiannis and N. Ramzan, “Dreamer: A database for emotion
recognition through eeg and ecg signals from wireless low-cost off-
the-shelf devices,” IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics,
vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 98–107, 2018.
S. Koelstra, C. Patras, Ioannis, A. Nijholt, M. Soleymani, T. Pun, J.-
S. Lee, A. Yazdani, and T. Ebrahimi, “DEAP: A database for emotion
analysis; Using physiological signals,” IEEE Transactions on Affective
Computing, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 18–31, 2012.
J. A. Miranda Correa, M. K. Abadi, N. Sebe, and I. Patras, “AMIGOS:
A Dataset for Affect, Personality and Mood Research on Individuals and
Groups,” IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, vol. 3045, no. i,
pp. 1–14, 2018.
A. Savran, K. Ciftci, G. Chanel, J. C. Mota, L. H. Viet, B. Sankur,
L. Akarun, A. Caplier, and M. Rombaut, “Emotion Detection in the
Loop from Brain Signals and Facial Images,” eNTERFACE, vol. 06,
no. January, pp. 69–80, 2006.
M. Soleymani, J. Lichtenauer, T. Pun, and M. Pantic, “A multimodal
database for affect recognition and implicit tagging,” IEEE Transactions
on Affective Computing, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 42–55, 2012.
L. A. Balam Guzman, Modelo semantico para la gestion de tecnicas
de HCI mediante el monitoreo de actividad bioelectrica (EEG) para
caracterizar estados mentales y su relacion con cambios en el contexto
del usuario. PhD thesis, Centro Nacional de Investigacion y Desarrollo
Tecnologico, 2015.
R. . W. . K. Jonathan Picard, “Computers that recognise and respond to
user emotion: theoretical and practical implications.,” Interacting with
computers, 2002.
J. Vila and M. Sanchez, “El Sistema Internacional de Imagenes Afectivas
(IAPS): Adaptacion española. Segunda parte.,” Revista de psicologia
general y aplicada, no. March 2015, 2001.
B. Mahesh, E. Prassler, T. Hassan, and J. U. Garbas, “Requirements for a
Reference Dataset for Multimodal Human Stress Detection,” 2019 IEEE
International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications
Workshops, PerCom Workshops 2019, pp. 492–498, 2019.
J. Y. Arana-Llanes, J. C. Rendon-Miranda, N. Gonzalez-Franco,
G. Gonzalez-Serna, and M. Lopez-Sanchez, “ExplotacioN De Estados
Cognitivos En Entornos E-Learning a Partir De Bci No Invasivas,”
No. September, pp. 1–6, 2015.
A. Claudia, E. Escobar, M. Isabel, L. Cañizo, and J. M. Aranalde, ““
La induccion de emociones a traves de ciertas escenas cinematograficas
en estudiantes mexicanos de preparatoria ”,” tech. rep., Academia de
ciencias de morelos, 2013.
Emotiv Sitio Oficial, “Emotiv,” 2017.
H. Madera-carrillo, D. Zarabozo, M. Ruiz-diaz, and P. Berriel-saez, “El
Sistema Internacional de Imagenes Afectivas ( IAPS ) en poblacion
mexicana,” tech. rep., 2015.
I. Mavridou, J. T. McGhee, M. Hamedi, M. Fatoorechi, A. Cleal,
E. Ballaguer-Balester, E. Seiss, G. Cox, and C. Nduka, “FACETEQ
interface demo for emotion expression in VR,” Proceedings - IEEE
Virtual Reality, pp. 441–442, 2017.
M. Schrepp, R. Otten, K. Blum, and J. Thomaschewski, “What causes
the dependency between perceived aesthetics and perceived usability?,”
International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelli-
gence, vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 78–85, 2021.
S. Majumder, S. Chowdhury, N. Dey, and K. C. Santosh, “Balance Your
Work-Life: Personal Interactive Web-Interface,” International Journal of
Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence, vol. In Press, no. In
Press, p. 1, 2021.
J. Nielsen, “Usability inspection methods,” Conference on Human Fac-
tors in Computing Systems - Proceedings, vol. 1994-April, pp. 413–414,
J. Soriano Terrazas, Metodologia para caracterizar e inducir estados
cognitivos y emocionales mediante realidad virtual inmersiva. PhD
thesis, Centro Nacional de Investigacion y Desarrollo Tecnologico, 2018.
D. Watson, L. A. Clark, and A. Tellegen, “Development and Validation
of Brief Measures of Positive and Negative Affect: The PANAS Scales,”
Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, vol. 54, 1988.
L. J. Cronbach, “Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests,”
Psychometrika, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 297–334, 1951.
C. Wohlin, P. Runeson, M. Höost, M. C. Ohlsson, B. Regnell, and
A. Wesslén, Experimentation in Software Engineering, vol. SE-12. 1986.
M. M. Bradley and P. J. Lang, “Measuring emotion: The self-assessment
manikin and the semantic differential,” Journal of Behavior Therapy and
Experimental Psychiatry, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 49–59, 1994.
M. H. Ost, B. J. Orn, and C. Wohlin, “Using Students as Subjects — A
Comparative Study of Students and Professionals in Lead-Time Impact
Assessment,” vol. 214, pp. 201–214, 2000.
J. Nielsen and R. Molich, “Heuristic evaluation of user interfaces,”
Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems - Proceedings,
no. April, pp. 249–256, 1990.
A. P. Manzano Patiño, “Introduccion a los modelos de ecuaciones
estructurales,” Investigacion en Educacion Medica, vol. 7, no. 25,
pp. 67–72, 2018