Efficient and Fast Wind Turbine MPPT Algorithm Using TS Fuzzy Logic and Optimal Relation Methods
Keywords:
Wind turbine system, MPPT algorithm, fuzzy logic, Takagi–Sugeno, optimal relation, F28069M board, PIL simulationAbstract
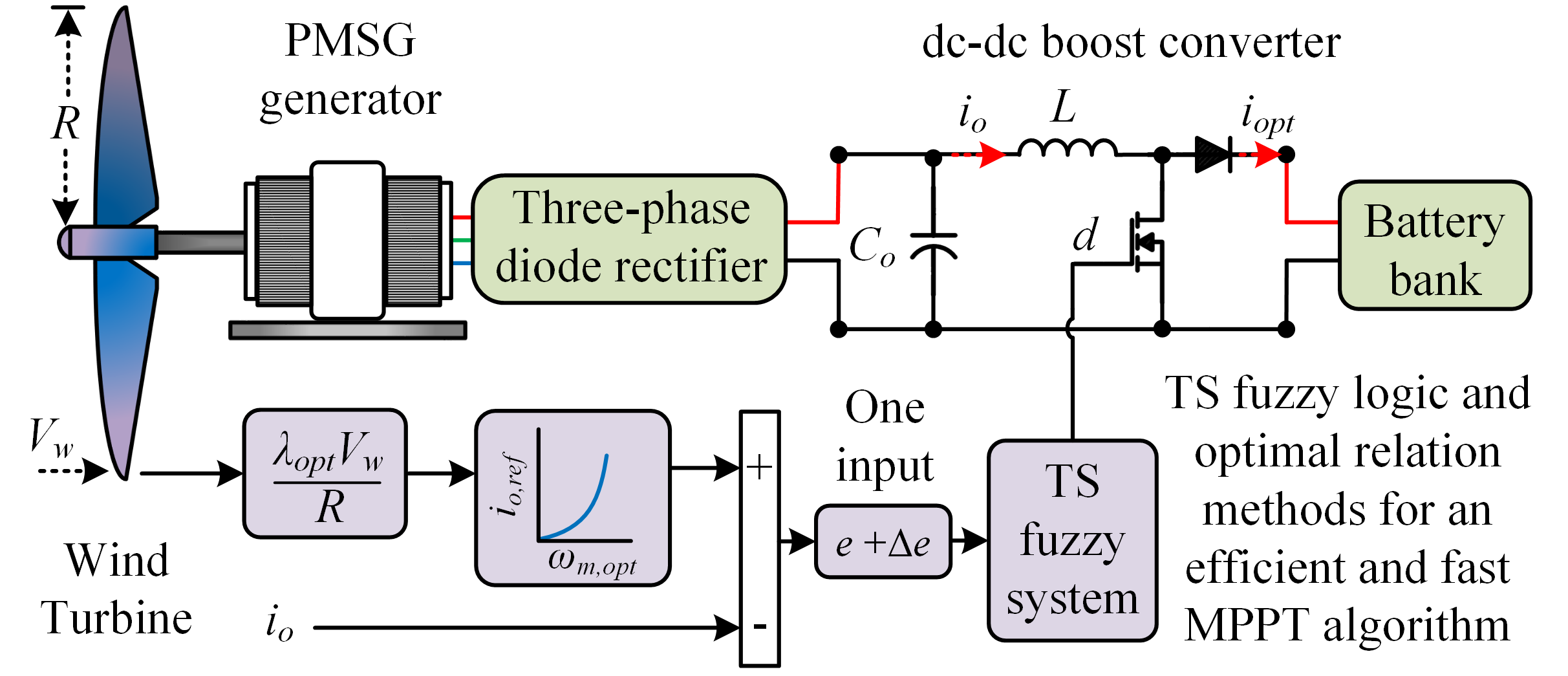
This paper proposes an efficient and fast maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithm for a wind turbine (WT) connected to a battery bank via a permanent magnet synchronous generator, a three-phase diode rectifier, and a dc-dc boost converter. The algorithm is based on the Takagi-Sugeno (TS) fuzzy system and optimal relation methods and is called TS-MPPT. The fuzzy system computes the converter duty cycle using an input that combines the error and its rate of change. The error is the difference between the reference current computed from the optimal relation and the rectifier current. The methods used in the algorithm resulted in a five-rule TS fuzzy system, which contributed to a fast algorithm in terms of its total execution time (TET): 89.12 µs on the F28069M board. The TET attained enabled a synchronized operation of the algorithm with the converter switching frequency. Additionally, the results based on the processor-in-the-loop simulation approach show that the TS-MPPT algorithm achieves an effective MPP tracking process with an energy conversion efficiency of 99.43% and behaves properly when evaluated over the typical WT power curve. Furthermore, the effectiveness and performance of the proposed algorithm are demonstrated against others using the proportional-integral controller, the Mamdani fuzzy method, and a TS fuzzy model from the literature.
Downloads
References
M. J. Khan, L. Mathew, M. A. Alotaibi, H. Malik, and M. E. Nassar, “Fuzzy-logic-based comparative analysis of different maximum power point tracking controllers for hybrid renewal energy systems,” Mathematics (Basel), vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 529–, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10030529.
M. A. Morales Caporal, J. d. J. Rangel Magdaleno, I. Cruz Vega, and R. Morales Caporal, “Improved grid-photovoltaic system based on variable-step MPPT, predictive control, and active/reactive control,” IEEE Latin America Transactions, vol. 15, no. 11, pp. 2064–2070, 2017. DOI:10.1109/TLA.2017.8070409.
A. A. Salem, N. A. N. Aldin, A. M. Azmy, and W. S. E. Abdellatif, “Implementation and validation of an adaptive fuzzy logic controller for MPPT of PMSG-based wind turbines,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 165690– 165707, 2021. DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3134947.
R. B. Bollipo, S. Mikkili, and P. K. Bonthagorla, “Hybrid, optimal, intelligent and classical PV MPPT techniques: A review,” CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 9–33, 2021. DOI:10.17775/CSEEJPES.2019.02720.
C. V. Govinda, S. V. Udhay, C. Rani, Y. Wang, and K. Busawon, “A review on various MPPT techniques for wind energy conversion system,” in 2018 International Conference on Computation of Power, Energy, Information and Communication (ICCPEIC), pp. 310–326, 2018. DOI:10.1109/ICCPEIC.2018.8525219.
M. Mao, L. Cui, Q. Zhang, K. Guo, L. Zhou, and H. Huang, “Classification and summarization of solar photovoltaic MPPT techniques: A review based on traditional and intelligent control strategies,” Energy reports, vol. 6, pp. 1312–1327, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2020.05.013.
X. C. Le, M. Q. Duong, and K. H. Le, “Review of the modern maximum power tracking algorithms for permanent magnet synchronous generator of wind power conversion systems,” Energies (Basel), vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 402–, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010402.
M. Oubella, M. Ajaampun, and B. Bouachrine, “Low cost microcontroller implementation of Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy MPPT controller for photovoltaic systems,” International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering Systems, vol. 13, no. 10, pp. 971–981, 2022. https: //doi.org/10.32985/ijeces.13.10.12.
M. H. Qais, H. M. Hasanien, and S. Alghuwainem, “Enhanced whale optimization algorithm for maximum power point tracking of variables peed wind generators,” Applied Soft Computing, vol. 86, p. 105937, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105937.
Z. Civelek, “Optimization of fuzzy logic (Takagi-Sugeno) blade pitch angle controller in wind turbines by genetic algorithm,” Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 1– 9, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2019.04.010.
L. L. Wang, “MPPT control for photovoltaic system based on T-S fuzzy reasoning,” in 2015 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT), pp. 1976–1980, 2015. DOI: 10.1109/DRPT.2015.7432562.
H. Abbes, H. Abid, and K. Loukil, “An improved MPPT incremental conductance algorithm using TS fuzzy system for photovoltaic panel,” International journal of renewable energy research, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 160–167, 2015. https://doi.org/10.20508/ijrer.v5i1.1868.g6481.
A. Jouda, F. Elyes, R. Abdelhamid, and M. Abdelkader, “Simulation and real implementation of the fuzzy MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic panel,” Indian Journal of Science and Technology, vol. 10, pp. 1–11, 2017. DOI:10.17485/ijst/2017/v10i17/90437.
H. Abid, A. Toumi, and M. Chaabane, “MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic panel based on augmented Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy model,” International Scholarly Research Notices, vol. 2014, pp. 1–10, 2014. https://doi.org/ 10.1155/2014/253146.
S. Abderrahim, M. Allouche, and M. Chaabane, “Intelligent power control of wind conversion system based on Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy model,” International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, vol. 51, no. 5, pp. 2247–2265, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/cta.3517.
M. Allouche, K. Dahech, M. Chaabane, and D. Mehdi, “T-S fuzzy control for MPPT of photovoltaic pumping system,” Journal of intelligent & fuzzy systems, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 2521–2533, 2018.
M. Allouche, K. Dahech, and M. Chaabane, “Multiobjective maximum power tracking control of photovoltaic systems: T-S fuzzy model-based approach,” Soft computing (Berlin, Germany), vol. 22, no. 7, pp. 2121– 2132, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2691-7.
D. Ounnas, M. Ramdani, S. Chenikher, and T. Bouktir, “An efficient maximum power point tracking controller for photovoltaic systems using Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy models,” Arabian journal for science and engineering (2011), vol. 42, no. 12, pp. 4971–4982, 2017. https: //doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2532-0.
D. R. Lopez-Flores, J. L. Duran-Gomez, and J. Vega-Pineda, “Discretetime adaptive PID current controller for wind boost converter,” IEEE Latin America Transactions, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 98–107, 2023. DOI:10.1109/TLA.2023.10015131.
K. Ogata, Sistemas de control en tiempo discreto. Pearson Educación, 1996.
S. Elert, “Programming possibilities using Matlab Simulink embedded coder on the example of data analysis from ahrs module,” Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol. 1507, p. 082042, mar 2020. DOI:10.1088/1742-6596/1507/8/082042.
S. Stipa, A. Ajay, D. Allaerts, and J. Brinkerhoff, “Tosca – an opensource, finite-volume, large-eddy simulation (les) environment for wind farm flows,” Wind Energy Science, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 297–320, 2024. https://doi.org/10.5194/wes-9-297-2024.
L. Legris, M. L. Pahus, T. Nishino, and E. Perez-Campos, “Prediction and mitigation of wind farm blockage losses considering mesoscale atmospheric response,” Energies, vol. 16, no. 1, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010386.