COVID-19 Vaccine’s distribution routes with bioinspired metaheuristic algorithms: Resoluteness
Keywords:
Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm, Bio-inspired, Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, Genetic Algorithm, Metaheuristics, Particle Swarm Optimization AlgorithmAbstract
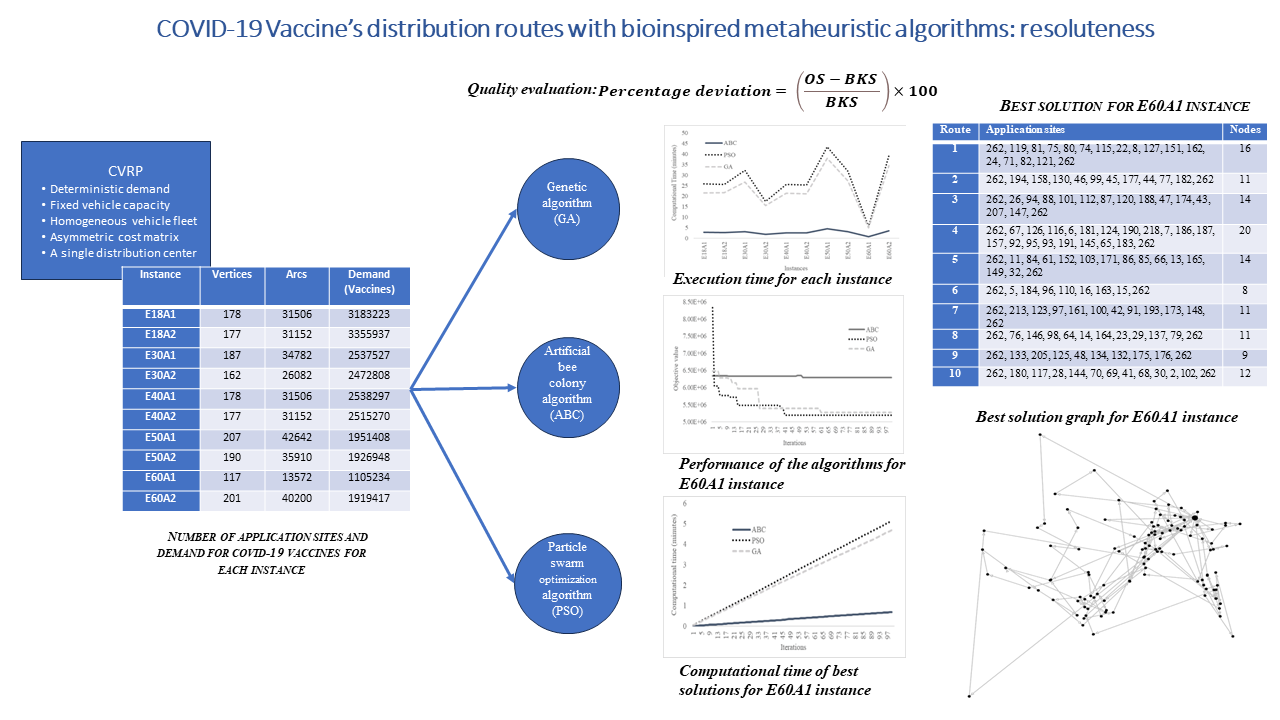
The global emergency of COVID-19 caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus at the end of 2019, was without a doubt a critical and historical point for society in general; for instance, the effective development of vaccines, as well as the efficient distribution of them; They were an unprecedented challenge to slow down the spread or mitigate its impact on societies around the world. This article specifies three bio-inspired metaheuristic algorithms (genetic algorithm, particle swarm optimization algorithm, and artificial bee colony algorithm) that were used in the context of the capacitated vehicle routing problem to generate vaccine distribution routes, specifically, COVID-19 vaccine for over 18 years old the first and the second doses applications in Mexico, particularly in the State of Mexico. The quality of the solutions obtained by these algorithms is compared, as a result of the performance of the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm being superior in solution quality.
Downloads
References
World Health Organization. “Coronavirus disease (COVID-19).” World Health Organization. Accessed: Feb. 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/question-and-answers-hub/q-a-detail/coronavirus-disease-covid-19
World Health Organization. “Origins of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.” World Health Organization. Accessed: Mar. 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/origins-of-the-virus
Banxico, “Reportes sobre las economías regionales Enero - Marzo 2020,” Banxico, Mexico, Accessed: Feb. 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.banxico.org.mx/publicaciones-y-prensa/reportes-sobre-las-economias-regionales/%7BAC9C8A70-ECC0-7B77-EE44-BE087567CB83%7D.pdf
Procuraduría Federal del Consumidor. “Nueva normalidad. Cuidarte es cuidar a los tuyos.” Gobierno de México. Accessed: Mar. 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.gob.mx/profeco/documentos/nueva-normalidad-cuidarte-es-cuidar-a-los-tuyos?state=published
World Health Organization. “WHO lists 9th COVID-19 vaccine for emergency use with aim to increase access to vaccination in lower-income countries.” World Health Organization. Accessed: Feb. 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/news/item/17-12-2021-who-lists-9th-covid-19-vaccine-for-emergency-use-with-aim-to-increase-access-to-vaccination-in-lower-income-countries
World Health Organization. “Vaccines and immunization: Vaccine safety.” World Health Organization. Accessed: Mar. 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/vaccines-and-immunization-vaccine-safety
R. Cortés Alcalá, R. Gómez Torres and X. Alba Ricaño, “Política nacional rectora de vacunación contra el SARS-CoV-2 para la prevención de la COVID-19 en México,” Gobierno de México, Mexico, Version 4.0, Accessed: Feb. 2022. [Online]. Available: https://coronavirus.gob.mx/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/PolVx_COVID_-11Ene2021.pdf
World Health Organization. “WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard.” World Health Organization. Accessed: Oct. 2023. [Online]. Available: https://covid19.who.int/
Secretaría de Salud de México. “Análisis situacional de la epidemia en México.” Gobierno de México. Accessed: Mar. 2023. [Online]. Available: https://coronavirus.gob.mx/analisis-situacional-de-la-epidemia-en-mexico/
G.D. Konstantakopoulos, S.P. Gayialis, and E.P. Kechagias, “Vehicle routing problem and related algorithms for logistics distribution: a literature review and classification,” Oper. Res., vol. 22, no. x, pp. 2033–2062, July. 2022, doi: 10.1007/s12351-020-00600-7.
X. Sun, C.-C. Wu, and L.-R. Chen, “Cold Chain Logistics Distribution Optimization for Fresh Processing Factory Based on Linear Programming Model,” in IAEAC., 2018, pp. 593-597, doi: 10.1109/IAEAC.2018.8577759.
B. Zhao, H. Gui, H. Li, and J. Xue, "Cold Chain Logistics Path Optimization via Improved Multi-Objective Ant Colony Algorithm," IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 142977-142995, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3013951.
L. Leng, J. Zhang, C. Zhang, Y. Zhao, W. Wang, and G. Li, “Decomposition-based hyperheuristic approaches for the bi-objective cold chain considering environmental effects,” Computers & Operations Res., vol. 123, no. 105043, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2020.105043.
S. Dou, G. Liu, and Y. Yang, "A New Hybrid Algorithm for Cold Chain Logistics Distribution Center Location Problem," IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 88769-88776, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990988.
W. Zheng, L. Leng, S. Wang, G. Li, and Y. Zhao, “A Hyperheuristic Approach for Location-Routing Problem of Cold Chain Logistics considering Fuel Consumption,” Comput. Intell. and Neuroscience, vol. 2020, no. 8395754, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1155/2020/8395754.
W.-C. Yeh and S.-Y. Tan, “The Vehicle Routing Problem: State-of-the-Art Classification and Review,” Appl. Sci., vol. 11, no. 10295, 2021, doi: 10.3390/app112110295.
J. Huang and T. Fei, “Optimization of Distribution Routes by Hybrid DNA-ACO Algorithm,” in AIAM., 2019, pp. 397-404, doi: 10.1109/AIAM48774.2019.00084.
M. Fu, T. Fei, L. Zhang, and H. Li, “Research on Location Optimization of Low-Carbon Cold Chain Logistics Distribution Center by FWA-Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm” in CISCE., 2021, pp. 529-533, doi: 10.1109/CISCE52179.2021.9446043
L. Zhang, M. Fu, T. Fei, and X. Pan, “Application of FWA-Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm in the Location of Low-Carbon Cold Chain Logistics Distribution Center in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Metropolitan Area,” Scientific Program., vol. 2021, no. 9945583, 2021, doi: 10.1155/2021/9945583.
K. Sujaree and N. Samattapapong, “A Hybrid Chemical Based Metaheuristic Approach for a Vaccine Cold Chain Network,” Operations and Supply Chain Management: An Int. J., vol. 14, pp. 351-359, 2021, doi: 10.31387/oscm0460307.
R. Torres, H. Perez, G. Perea, and I. Soria-Arguello, “A Proposal Mathematical Model for the Vaccine COVID-19 Distribution Network: A Case Study in Mexico”, Math. Problems in Eng., vol. 2021, 2021, Art. no. 5484101, doi: 10.1155/2021/5484101
P. Toth and D. Vigo, THE VEHICLE ROUTING PROBLEM. PA, USA: SIAM, 2002.
H. Zhang, H. Ge, J. Yang, and Y. Tong, “Review of Vehicle Routing Problems: Models, Classification and Solving Algorithms,” Archives of Comput. Methods in Eng., vol. 29, pp. 195–221 , 2022, doi: 10.1007/s11831-021-09574-x.
S. Katoch, S. S. Chauhan, and V. Kumar, “A review on genetic algorithm: past, present, and future,” Multimedia Tools and Appl., vol. 80, pp. 8091–8126, 2021, doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-10139-6.
K.-L. Du and M. N. S. Swamy, Search and Optimization by Metaheuristics: Techniques and Algorithms Inspired by Nature. Switzerland: Birkhäuser Cham, 2016.
N. Bacanin et al., "Artificial Neural Networks Hidden Unit and Weight Connection Optimization by Quasi-Refection-Based Learning Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm," IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 169135-169155, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3135201.
T. M. Shami, A. A. El-Saleh, M. Alswaitti, Q. Al-Tashi, M. A. Summakieh, and S. Mirjalili, "Particle Swarm Optimization: A Comprehensive Survey," in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 10031-10061, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3142859.
C. So-In, K. Rujirakul, P. Aimtongkham, and C. Punriboon, “A Bio-Inspired Capacitated Vehicle-Routing Problem Scheme Using Artificial Bee Colony with Crossover Optimizations,” J. of Internet Services and Inf. Secur., vol. 9, pp. 21-40, 2019, doi: 10.22667/JISIS.2019.08.31.021.
J. Pasha et al., “Exact and metaheuristic algorithms for the vehicle routing problem with a factory-in-a-box in multi-objective settings,” Adv. Eng. Inform., vol. 52, no. 101623, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2022.101623.
J. Pasha, M. A. Dulebenets, M. Kavoosi, O. F. Abioye, H. Wang, and W. Guo, "An Optimization Model and Solution Algorithms for the Vehicle Routing Problem With a “Factory-in-a-Box”," IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 134743-134763, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3010176.
Gobierno del Estado de México. Portal Cuidadano del Gobierno del Estado de México. Accessed: 2022. [Online]. Available: https://edomex.gob.mx/vacunacion.
Google. “Google Maps.” Google. Accessed: 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.google.com.mx/maps/preview.
Sistema Nacional de Información Estadística y Geográfica. Instituto
Nacional de Información Estadística y Geográfica - INEGI. Accessed: 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.inegi.org.mx/temas/estructura/
Google. “Google Maps Platform.” Google. Accessed: 2022. [Online]. Available: https://developers.google.com/maps
P. Augerat, 1995, “Augerat 1995 - Set A,” VRP-REP. [Online]. Available: http://www.vrp-rep.org/datasets/item/2014-0000.html
P. Augerat, 1995, “Augerat 1995 - Set B,” VRP-REP. [Online]. Available: http://www.vrp-rep.org/datasets/item/2014-0001.html
P. Augerat, 1995, “Augerat 1995 - Set P,” VRP-REP. [Online]. Available: http://www.vrp-rep.org/datasets/item/2014-0009.html
World Health Organization. “Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, COMIRNATY® (Tozinameran).” World Health Organization. Accessed: Sept. 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/comirnaty-covid-19-mrna-vaccine
World Health Organization. “COVID-19 Vaccine Moderna (mRNA-1273).” World Health Organization. Accessed: Sept. 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-vaccine-moderna-mrna-1273