Advanced metering infrastructure system and massive data simulation, based on the smart grid concept.
Keywords:
Advanced metering infrastructure, power factor correction, data simulation.Abstract
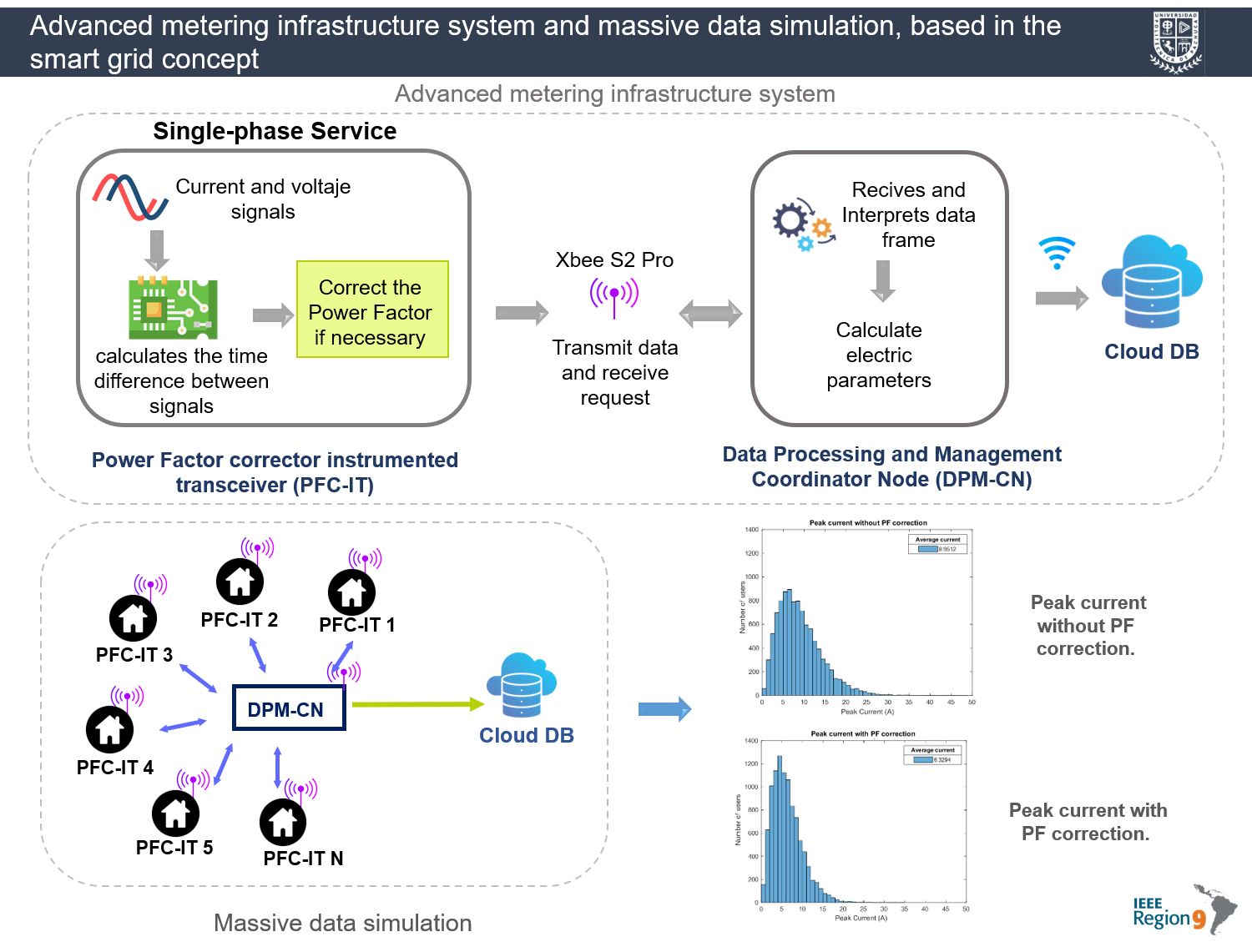
An advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) system has been designed to measure electrical parameters and transmit them to a database (DB) on the smart grid (SG) concept. The present system allows remote monitoring of electrical parameters for a single-phase residential service, able to automatically correct the power factor (PF) and upload information to a DB. The system’s performance has been tested by calculating non-homogeneous parameters of ten thousand residential users to simulate its massive operation. The geographical coverage of more than two thousand users clustered as a private wireless network can be ensured in line-of-sight. It has been estimated the reduction of average current consumption around 29%. Collected data in the DB can be used for modeling and optimization purposes in electricity generation and distribution according to demand-side management techniques.
Downloads
References
M. H. Maruf, M. A. ul Haq, S. K. Dey, A. Al Mansur, y A. S. M. Shihavuddin, “Adaptation for sustainable implementation of Smart Grid in developing countries like Bangladesh”, Energy Rep., vol. 6, pp. 2520–2530, nov. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2020.09.010.
A. K. Dsouza, A. Thammaiah, y L. K. M. Venkatesh, “An intelligent management of power flow in the smart grid system using hybrid NPO-ATLA approach”, Artif. Intell. Rev., vol. 55, núm. 8, pp. 6461–6503, dic. 2022, doi: 10.1007/s10462-022-10158-9.
E. Kabalcı, Y. Kabalcı, y P. Siano, “Design and implementation of a smart metering infrastructure for low voltage microgrids”, Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst., vol. 134, p. 107375, ene. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2021.107375.
S. Yilmaz, A. Rinaldi, y M. K. Patel, “DSM interactions: What is the impact of appliance energy efficiency measures on the demand response (peak load management)?”, Energy Policy, vol. 139, p. 111323, abr. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111323.
James Momoh, Smart Grid. Fundamentals of Design and Analysis, 1a ed. United States of America: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 2012.
O. Abrishambaf, P. Faria, y Z. Vale, “Ramping of Demand Response Event with Deploying Distinct Programs by an Aggregator”, Energies, vol. 13, núm. 6, Art. núm. 6, ene. 2020, doi: 10.3390/en13061389.
T. Zhang, X. Ji, y W. Xu, “Jamming-Resilient Backup Nodes Selection for RPL-based Routing in Smart Grid AMI Networks”, Mob. Netw. Appl., vol. 27, núm. 1, pp. 329–342, feb. 2022, doi: 10.1007/s11036-020-01634-z.
Z. Xu, Y. Gao, M. Hussain, y P. Cheng, “Demand Side Management for Smart Grid Based on Smart Home Appliances with Renewable Energy Sources and an Energy Storage System”, Math. Probl. Eng., vol. 2020, p. e9545439, abr. 2020, doi: 10.1155/2020/9545439.
M. U. Saleem, M. R. Usman, M. A. Usman, y C. Politis, “Design, Deployment and Performance Evaluation of an IoT Based Smart Energy Management System for Demand Side Management in Smart Grid”, IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 15261–15278, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3147484.
S. de Energía, “Programa para el Desarrollo del Sistema Eléctrico Nacional 2022-2036”, gob.mx, el 31 de mayo de 2022. http://www.gob.mx/sener/articulos/programa-para-el-desarrollo-del-sistemaelectrico-nacional-304042 (consultado el 14 de agosto de 2022).
“Portal CFE-Información al cliente”, Información al cliente - Conoce tu recibo. https://www.cfe.mx/hogar/infcliente/pages/conoceturecibo.aspx (Accessed 11 January 2023).
Comisión Federal de Electricidad, “Plan de Negocios 2023-2027 Pública”. diciembre de 2022. [Available online]: https://www.cfe.mx/finanzas/Documents/Plan_Negocios_2023-2027.pdf
H. P. Devarapalli, V. S. S. S. S. Dhanikonda, y S. B. Gunturi, “Non-Intrusive Identification of Load Patterns in Smart Homes Using Percentage Total Harmonic Distortion”, Energies, vol. 13, núm. 18, Art. núm. 18, ene. 2020, doi: 10.3390/en13184628.
I. González, A. J. Calderón, y F. J. Folgado, “IoT real time system for monitoring lithium-ion battery long-term operation in microgrids”, J. Energy Storage, vol. 51, p. 104596, jul. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.est.2022.104596.
K. T., C. R. S., J. D. N. J., y C. K., “Design of IoT based smart compact energy meter for monitoring and controlling the usage of energy and power quality issues with demand side management for a commercial building”, Sustain. Energy Grids Netw., vol. 26, p. 100454, jun. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.segan.2021.100454.
S. A. Hashmi, C. F. Ali, y S. Zafar, “Internet of things and cloud computing-based energy management system for demand side management in smart grid”, Int. J. Energy Res., vol. 45, núm. 1, pp. 1007–1022, 2021, doi: 10.1002/er.6141.
M. Forcan, M. Maksimović, J. Forcan, y S. Jokić, “5G and Cloudification to Enhance Real-Time Electricity Consumption Measuring in Smart Grid”, en 2020 28th Telecommunications Forum (℡FOR), nov. 2020, pp. 1–4. doi: 10.1109/℡FOR51502.2020.9306518.
Y. Song, P.-Y. Kong, Y. Kim, S. Baek, y Y. Choi, “Cellular-Assisted D2D Communications for Advanced Metering Infrastructure in Smart Gird”, IEEE Syst. J., vol. 13, núm. 2, pp. 1347–1358, jun. 2019,
doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2891719.
R. Arrieta-Pérez, C. Fragoso-Cruz, A. Meneses-Figueroa, y D. Robles-Camarillo, “Sistema electrónico para monitoreo de la demanda y corrección del factor de potencia para servicio eléctrico residencial”, núm. 9, p. 8, 2021.
U. Nations, “Objetivo 13—La adopción de medidas urgentes para combatir el cambio climático – los ODS y el acuerdo de París sobre el clima | Naciones Unidas”, United Nations, 2016.
https://www.un.org/es/chronicle/article/objetivo-13-la-adopcion-de-medidasurgentes-para-combatir-el-cambio-climatico-los-ods-y-el-acuerdo (Accessed 20 november 2022).
U. Nations, “Objetivo 7—Garantizar el acceso a una energía asequible, fiable, sostenible y moderna para todos | Naciones Unidas”, United Nations, el 25 de septiembre de 2015. https://www.un.org/es/chronicle/article/objetivo-7-garantizar-el-acceso-una-energia-asequible-fiable-sostenible-y-moderna-paratodos (Accessed 2 august 2022).
C. K. Alexander y M. N. O. Sadiku, Fundamentos de Circuitos Eléctricos, 5a ed. México, D.F.: McGRAW-HILL/INTERAMERICANA EDITORES, S.A. de C.V., 2006.
T. L. Floyd, Principios de Circuitos Eléctricos, 8va. Naucalpan de Juárez, Edo. de México: Pearson Educación de México, S.A. de C.V., 2007.
D. Robles-Camarillo, “Solicitud de Patente ‘Sistema inteligente de monitoreo de parámetros eléctricos para acometida monofásica con corrección del factor de potencia”. 2022.
“Module User Guide - Router/Coordinator configuration Xbee-PRO”. https://www.digi.com/resources/documentation/digidocs/90002002/default.ht
m#Containers/cont_xbee_pro_zigbee_router_coord_config.htm?TocPath=Ma
nage%2520End%2520Devices%257CRouter%252FCoordinator%2520config
uration%257C_____0 (Accessed 23 February 2023).
“Primeros pasos con Cloud Firestore”, Firebase. https://firebase.google.com/docs/firestore/quickstart?hl=es-419 (Accessed 14 august 2022).
R. Buyya, C. Vecchiola, y S. T. Selvi, Mastering cloud computing: foundations and applications programming. Ámsterdam ; Boston: Morgan Kaufmann, 2013.
“Django”, Django Project. https://www.djangoproject.com/ (Accessed 2 may 2023).
E. Lee, J. Kim, y D. Jang, “Load Profile Segmentation for Effective Residential Demand Response Program: Method and Evidence from Korean Pilot Study”, Energies, vol. 13, núm. 6, Art. núm. 6, ene. 2020, doi: 10.3390/en13061348.
DOF - Diario Oficial de la Federación, “PROYECTO de Norma Oficial Mexicana PROY-NOM-001-SEDE-2018, Instalaciones Eléctricas 9 ID 8215
(utilización)”, el 6 de agosto de 2018. https://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5533986&fecha=06/08/2018 (Accessed 29 november 2022).
D. C. Montgomery, Diseño y análisis de experimentos, 2a ed. México, D.F.: Limusa Wiley, 2004.
INEGI, “Espacio y datos de México”, Accessed 20 January 2023, [Available online:] https://www.inegi.org.mx/app/mapa/espacioydatos/
Market Data Mexico, “Perfil sociodemográfico: Colonia San Cayetano, Pachuca de Soto, en Hidalgo”, Accessed 20 January 2023, [Available online:] https://www.marketdatamexico.com/es/article/Perfil-sociodemografico-
Colonia-San-Cayetano-Pachuca-Soto-Hidalgo
C. Gavilanez, M. Jaramillo, W. Pavón, C. Barrera-Singaña, and M. Ruíz, “Power Factor Improvement in a Distribution System by Implementing Adaptive Control for Reactive Power Filters,” in 2022 IEEE Global Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GlobConPT), 2022,
pp. 1–6, doi: 10.1109/GlobConPT57482.2022.9938312.
M. Callacando, W. Pavón, and L. Ortíz, “Multilevel inverter DSTATCOM for reducing total harmonic distortion in a non-linear loads electrical distribution system,” Rev. Técnica "energía", vol. 19, no. 1 SE-EFICIENCIA ENERGÉTICA, p. PP. 85-91, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.37116/revistaenergia.v19.n1.2022.520.