Advanced Metering Infrastructure for Industrial Natural Gas Smart Management
Keywords:
Internet of Things, LoRaWAN, Anomaly Detection, Natural Gas MeasurementAbstract
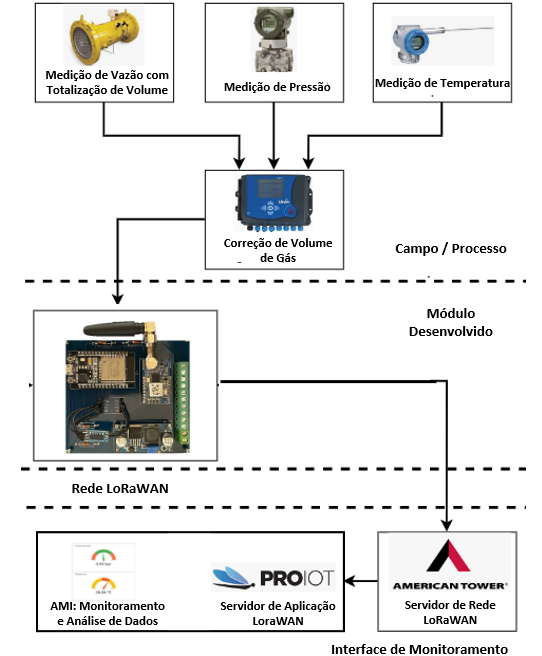
One of the challenges within the utilities sector is the development of robust, scalable and low-cost methods for the remote management of customers usage and billing. Considering the advances related to the Internet of Things (IoT), an Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) is the basis for utilities smart management. This AMI bring together the automation of remote metering and communication infrastructures with the processing and analysis of distributed data using advanced techniques and cloud computing. This paper presents the development of an AMI for the smart management of natural gas industrial customers using IoT. The AMI architecture is based on the LoRaWAN communication for remote metering and a cloud-based smart management system including supervisory control, continuous monitoring, anomalies detection and alarm notification. Experimental results shown the LoRaWAN fulfilled the communication requirements for industrial natural gas metering and the smart management system can analyze historical data and detect anomalies in gas consumption
Downloads
References
F. V. Schreiber et al., "Application of the IoT Paradigm for Supervision in the Utilities Industry," 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Industry Applications, pp. 864-869, 2018, doi: 10.1109/INDUSCON.2018.8627211.
C. Nugroho and G. Wibisono, "NB-IoT Planning in Jakarta Area for Smart Meter Utilities," 2019 IEEE International Conference on Innovative Research and Development, pp. 1-6, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ICIRD47319.2019.9074629.
B. S. Chaudhari, M. Zennaro, and S. Borkar, “LPWAN Technologies: Emerging Application Characteristics, Requirements, and Design Considerations,” Future Internet, vol. 12, no. 3, p. 46, 2020, doi: 10.3390/fi12030046.
J. Chan, R. Ip, K. W. Cheng and K. S. P. Chan, "Advanced Metering Infrastructure Deployment and Challenges," 2019 IEEE PES GTD Grand International Conference and Exposition Asia, pp. 435-439, 2019, doi: 10.1109/GTDAsia.2019.8715927.
Z. Wang et al, "Ultralow-Power Sensing Framework for Internet of Things: A Smart Gas Meter as a Case," IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 9, no. 10, pp. 7533-7544, 2022 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3110886.
V. Gomathy et al, “Internet of Things‐Based Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) for Smart Grids,” Integration of Renewable Energy Sources with Smart Grid, pp. 77-100, 2021 doi; 10.1002/9781119751908.ch4.
LoRa Alliance, "Why Utilities are choosing Smart LoRaWAN® connectivity”, https://lora-alliance.org/resource_hub/why-utilities-are-choosing-smart-lorawan-connectivity/ (Acesso em 23-11-2022).
A. Ikpehai et al., "Low-Power Wide Area Network Technologies for Internet-of-Things: A Comparative Review," IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 2225-2240, 2019, doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2883728.
J. L. Gallardo, M. A. Ahmed and N. Jara, "LoRa IoT-Based Architecture for Advanced Metering Infrastructure in Residential Smart Grid," IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 124295-124312, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3110873.
CPFL, Companhia Paulista de Força e Luz “CPFL Investor Day 2020” CPFL. https://cpfl.riweb.com.br/Download.aspx?Arquivo=XtQj nCDzLSfKhn7+fdhb9Q== (Acesso em 17-12-2022).
SABESP, Companhia de Saneamento Básico do Estado de São Paulo, Everynet apoia a implantação de medidores inteligentes de água pela SABESP e LAAGER no Brasil”. https://www.everynet.com/blog/everynet-apoia-implantacao-de-medidores-inteligentes-de-agua-pela-sabesp-e-laager-no-brasil (Acesso em: 10-12-2022).
ABEGAS, Associação Brasileira das Empresas Distribuidoras de Gás Canalizado, “Comgás quer ter medição remota do consumo para 100% dos clientes”. https://www.abegas.org.br/arquivos/82714. (Acesso em 24-12-2022).
ATC, American Tower, “Rede Neutra ATC LoRaWAN”. ATC. https://americantower.com.br/pt/soluções/rede-neutra-loRaWAN.html (Acesso em: 12-12-2022)
Z. Ullah et al., “Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning in smart cities”, Computer Communications, vol. 154, pp. 313-323, 2020, doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2020.02.069.
ABINC, Associação Brasileira de Internet das Coisas, “Panorama de IoT em Utilities no Brasil”. ABINC, https://abinc.org.br/noticias/abinc-realiza-webinar-sobre-iot-em-utilities (Acesso em: 10-12-2022)
Conversores de volume de gás – Terminologia, classificação, faixas de medição e condições estipuladas de funcionamento, NBR 14978 Parte 1, Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas – ABNT, 2020.
J. A. Micheletti and E. P. Godoy, "Improved Indoor 3D Localization using LoRa Wireless Communication," in IEEE Latin America Transactions, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 481-487, March 2022, doi: 10.1109/TLA.2022.9667147.
N. C. Almeida et al., "Proposal of a Hybrid LoRa Mesh / LoRaWAN Network," 2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT, 2020, pp. 702-707, doi: 10.1109/MetroInd4.0IoT48571.2020.9138206.
ProIot, "Plataforma de IoT com conectividade LoRaWAN". ProIoT. https://proiot.com.br/aplicacao (Acesso em 22-06-2022).
P. J. Basford et al., “LoRaWAN for Smart City IoT Deployments: A Long Term Evaluation,” Sensors, vol. 20, no. 3, p. 648, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.3390/s20030648.