Input vector selection in NARX models using statistical techniques to improve the generated power forecasting in PV systems
Keywords:
Neural Network, Electrical Power, Input Vector, Photovoltaic System, Collinearity and Granger TestsAbstract
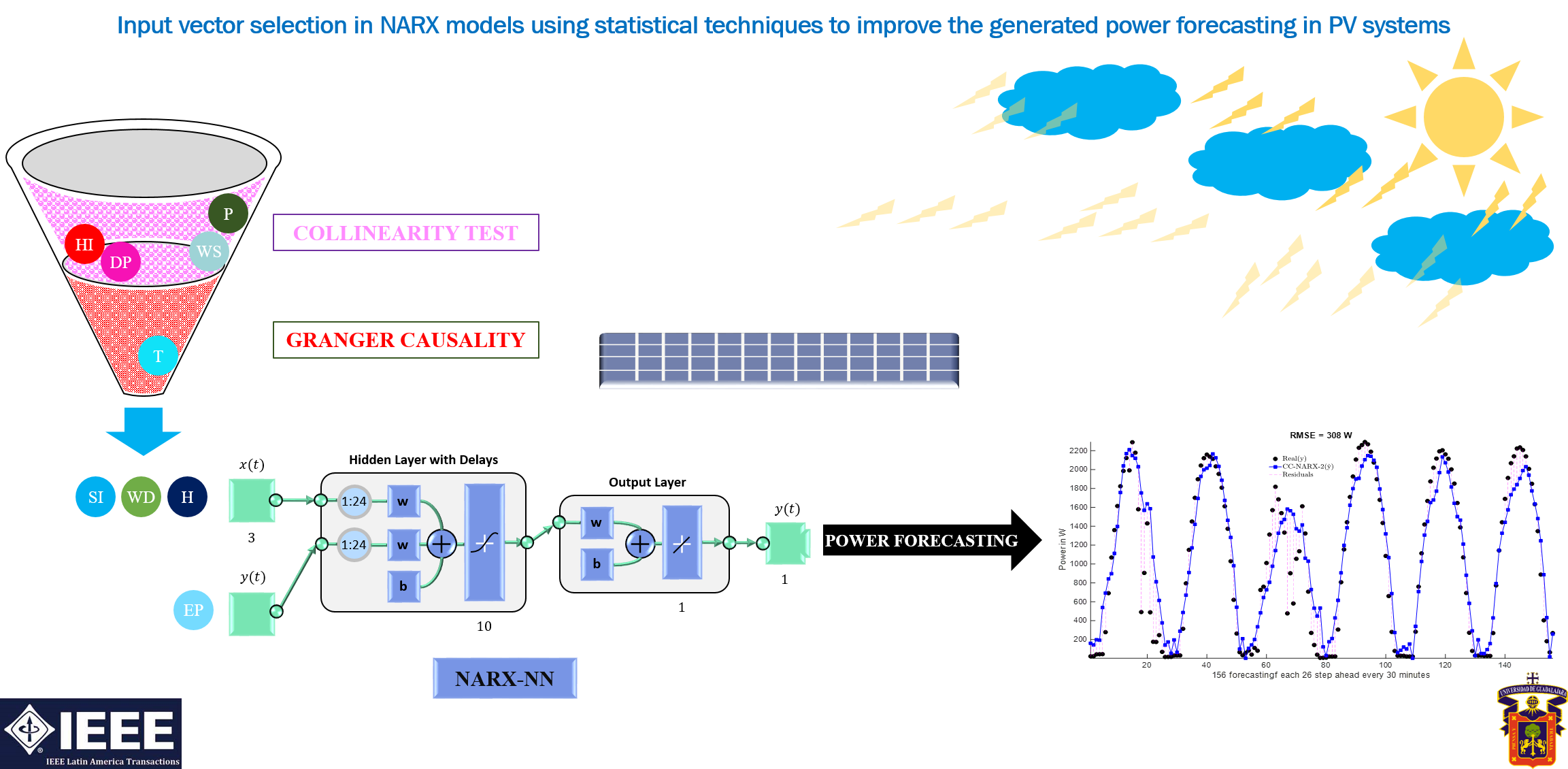
This paper uses collinearity and causality tests to choose variables for an input vector to forecast the electrical power generated by a photovoltaic system. The collinearity test determines redundant variables, and the causality test determines which variables cause the electric power. The chosen input vector is used to train nonlinear autoregressive models with external inputs neural networks (NARX-NN). We develop an algorithm to generate NARX models with an all variable combinations algorithm (AVCA) to validate the results. Finally, we compare the results of the proposed methodology against the best results obtained by the AVCA; the algorithm tests 502 input vectors with the NARX model to forecast 26 steps (a day ahead) of the electrical power. The best model chosen using the collinearity and causality techniques has an RMSE of 308 W for the electric power using four variables in the input vector; the best model using the AVCA has an RMSE of 305 W using five variables in the input vector. Results show that the collinearity and causality techniques are a direct way to select the input vector without affecting the model’s performance and results in a reduction of the input vector length.
Downloads
References
N. S. Maimouna Diagne, Mathieu David, Philippe Lauret, John Boland, “Review of solar irradiance forecasting methods and proposition for small-scale insular grids,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 27, pp. 65–76, 2013.
P. F. Jiménez-Pérez and L. Mora-López, “Modeling and forecasting hourly global solar radiation using clustering and classification techniques,” Solar Energy, vol. 135, pp. 682–691, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2016.06.039.
F. O. Hocaoglu and F. Karanfil, “A time series-based approach for renewable energy modeling,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 28, pp. 204–214, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.07.054.
H. Eom, Y. Son, and S. Choi, “Feature-selective ensemble learning-based long-term regional PV generation forecasting,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 54620–54630, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2981819.
E. Rangel, E. Cadenas, R. Campos-Amezcua, and J. L. Tena, “Enhanced prediction of solar radiation using NARX models with corrected input vectors,” Energies (Basel), vol. 13, no. 10, pp. 1–22, 2020, doi: 10.3390/en13102576.
E. Rangel-Heras, C. Angeles-Camacho, E. Cadenas-Calderón, and R. Campos-Amezcua, “Short-Term Forecasting of Energy Production for a Photovoltaic System Using a NARX-CVM Hybrid Model,” Energies (Basel), vol. 15, no. 8, Apr. 2022, doi: 10.3390/en15082842.
S. Hussain and A. Al-Alili, “A new approach for model validation in solar radiation using wavelet, phase and frequency coherence analysis,” Appl Energy, vol. 164, pp. 639–649, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.12.038.
M. Louzazni, H. Mosalam, and A. Khouya, “A non-linear auto-regressive exogenous method to forecast the photovoltaic power output,” Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, vol. 38, Apr. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.seta.2020.100670.
M. Louzazni, H. Mosalam, and D. T. Cotfas, “Forecasting of photovoltaic power by means of non-linear auto-regressive exogenous artificial neural network and time series analysis,” Electronics (Switzerland), vol. 10, no. 16, Aug. 2021, doi: 10.3390/electronics10161953.
A. Ahmad, T. N. Anderson, and T. T. Lie, “Hourly global solar irradiation forecasting for New Zealand,” Solar Energy, vol. 122, pp. 1398–1408, 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2015.10.055.
L. Yanting, S. Yan, and S. Lianjie, “An ARMAX model for forecasting the power output of a grid connected photovoltaic system,” Renew Energy, vol. 66, pp. 78–89, 2014.
V. Sharma, D. Yang, W. Walsh, and T. Reindl, “Short term solar irradiance forecasting using a mixed wavelet neural network,” Renew Energy, vol. 90, pp. 481–492, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2016.01.020.
L. Liu, M. Zhan, and Y. Bai, “A recursive ensemble model for forecasting the power output of photovoltaic systems,” Solar Energy, vol. 189, pp. 291–298, Sep. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2019.07.061.
M. Alkandari and I. Ahmad, “Solar power generation forecasting using ensemble approach based on deep learning and statistical methods,” Solar power generation forecasting, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.aci.
T. Chuluunsaikhan, A. Nasridinov, W. Seok-Choi, D. bin Choi, S. Hyun Choi, and Y. Myoung Kim, “Predicting the Power Output of Solar Panels based on Weather and Air Pollution Features using Machine Learning,” Journal of Korea Mutilmedia Society, vol. 24, pp. 222–232, 2021.
P. Dawan et al., “Comparison of power output forecasting on the photovoltaic system using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems and particle swarm optimization-artificial neural network model,” Energies (Basel), vol. 13, no. 2, 2020, doi: 10.3390/en13020351.
R. Azimi, M. Ghayekhloo, and M. Ghofrani, “A hybrid method based on a new clustering technique and multilayer perceptron neural networks for hourly solar radiation forecasting,” Energy Convers Manag, vol. 118, pp. 331–344, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2016.04.009.
J. Boland, M. David, and P. Lauret, “Short term solar radiation forecasting: Island versus continental sites,” Energy, vol. 113, pp. 186–192, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.06.139.
S. Monjoly, M. André, R. Calif, and T. Soubdhan, “Hourly forecasting of global solar radiation based on multiscale decomposition methods: A hybrid approach,” Energy, vol. 119, pp. 288–298, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.11.061.
C.-R. Chen and U. Kartini, “k-Nearest Neighbor Neural Network Models for Very Short-Term Global Solar Irradiance Forecasting Based on Meteorological Data,” Energies (Basel), vol. 10, no. 2, p. 186, 2017, doi: 10.3390/en10020186.
A. A. du Plessis, J. M. Strauss, and A. J. Rix, “Short-term solar power forecasting: Investigating the ability of deep learning models to capture low-level utility-scale Photovoltaic system behaviour,” Appl Energy, vol. 285, Mar. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.116395.
J. Huang and R. J. Davy, “Predicting intra-hour variability of solar irradiance using hourly local weather forecasts,” Solar Energy, vol. 139, pp. 633–639, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2016.10.036.
E. Akarslan and F. O. Hocaoglu, “A novel adaptive approach for hourly solar radiation forecasting,” Renew Energy, vol. 87, pp. 628–633, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2015.10.063.
K. Benmouiza and A. Cheknane, “Small-scale solar radiation forecasting using ARMA and nonlinear autoregressive neural network models,” Theor Appl Climatol, vol. 124, no. 3–4, pp. 945–958, 2016, doi: 10.1007/s00704-015-1469-z.
D. C. Montgomery, C. L. Jennings, and M. Kulahci, Introduction to Time Series Analysis and Forecasting, Second. New Jersey: Wiley, 2015. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-28725-6.
N. M. Noor, M. M. al Bakri Abdullah, A. S. Yahaya, and N. A. Ramli, “Comparison of linear interpolation method and mean method to replace the missing values in environmental data set,” in Materials Science Forum, 2015, vol. 803, pp. 278–281. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.803.278.
J. Honaker et al., “What to Do about Missing Values in Time-Series Cross-Section Data,” Am J Pol Sci, vol. 54, no. 2, pp. 561–581, 2010, [Online]. Available: http://gking.harvard.edu
R. E. Shiffler, “Maximum z scores and outliers,” American Statistician, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 79–80, 1988, doi: 10.1080/00031305.1988.10475530.
D. Cousineau and S. Chartier, “Outliers detection and treatment: a review,” Int J Psychol Res (Medellin), vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 58–67, 2010, [Online]. Available: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=299023509004
D. Belsley, E. Kuh, and R. Welsch, Regression Diagnostics — Identifying Influential Data and Sources of Collinearity, vol. 32, no. 2. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1980.
D. N. Gujarati and D. C. Porter, Basic Econometrics, 5th ed. Douglas Reiner, 2009.
S. G. Makridakis, S. C. Wheelwright, and R. J. Hyndman, Forecasting Methods and Applications, 3rd ed. Wiley, 1997.
M. Yang, “Lag length and mean break in stationary VAR models,” Econom J, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 374–386, 2002, [Online]. Available: http://www.jstor.orgURL:http://www.jstor.org/stable/23114900http://www.jstor.org/page/info/about/policies/terms.jsp
J. Durbin and G. S. Watson, “Testing for Serial Correlation in Least Squares Regression: I,” Springer, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 237–259, 1992, [Online]. Available: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2332391