Predictive Performance of Machine Learning Algorithms Regarding Obesity Levels Based on Physical Activity and Nutritional Habits: A Comprehensive Analysis
Keywords:
Artificial Neural Networks, Obesity, Machine LearningAbstract
Obesity is a complex chronic disease resulting from the interaction of multiple behavioral factors. This paper presents
the application of Machine Learning to identify the primary groups of behaviors contributing to the development of obesity.
Supervised machine learning emphasizes decision trees and deep artificial neural networks from datasets. The study also references
related work that utilizes predictive methods to estimate obesity levels based on physical activity and dietary habits. Furthermore,
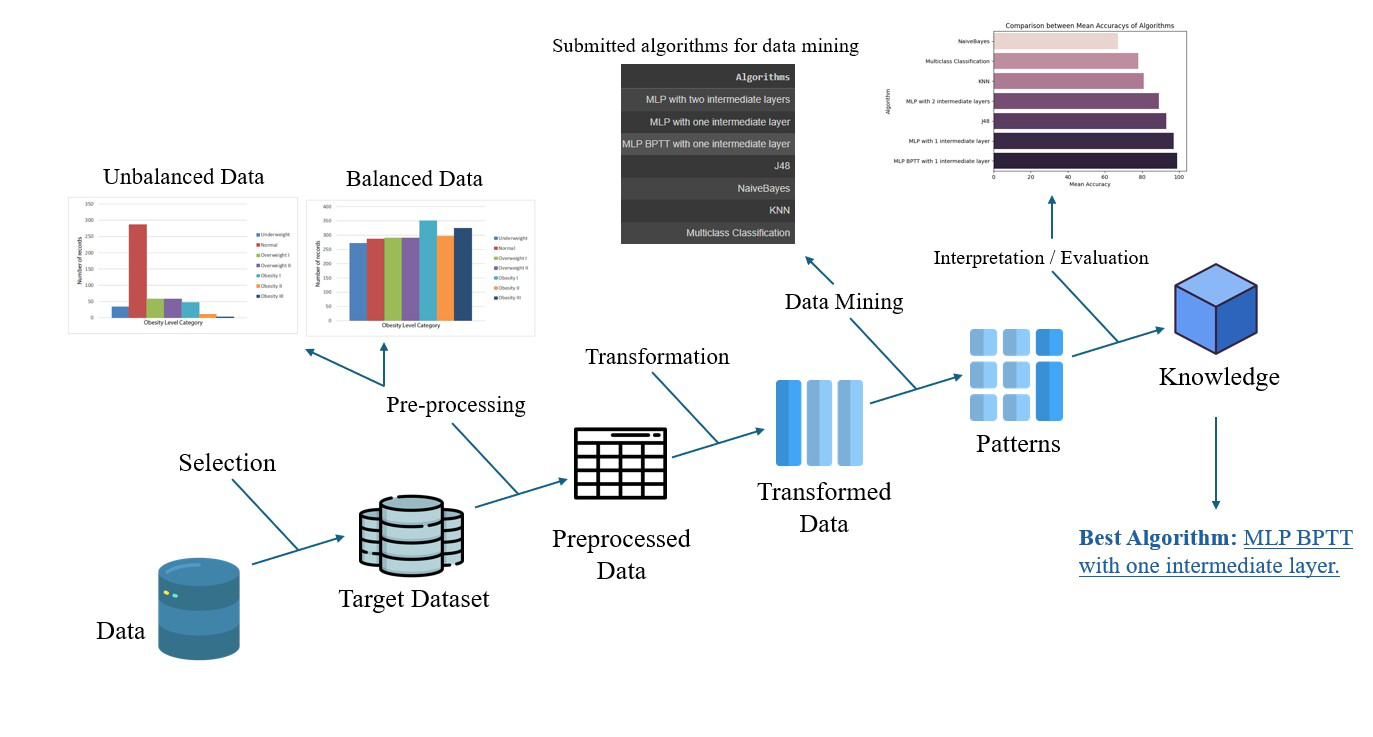
it compares the performance of classification algorithms such as J48, Naive Bayes, Multiclass Classification, Multilayer Perceptron, KNN, and decision trees when predicting diabetes cases. The objective is to analyze different tools in the assessment based on physical activity and dietary habits, contributing to the improvement of obesity risk diagnosis. In addition, MLP and J48 demonstrated strong performance among all the algorithms, but BPTT achieved the highest overall performance.
Downloads
References
J. F. López-Gil, S. M. Wu, T.-L. I. Lee, C.-W. Shih, S. Tausi, V. Sosene,
P. P. Maani, M. Tupulaga, Y.-T. Hsu, C.-R. Chang, S.-C. Shiau, Y.-H. Lo,
C.-F. Wei, P.-J. Lin, and M. S. Hershey, “Higher imported food patterns
are associated with obesity and severe obesity in tuvalu: A latent class
analysis,” Current Developments in Nutrition, p. 102080, 1 2024, doi:
1016/j.cdnut.2024.102080.
A. S. Kelly, S. E. Barlow, G. Rao, T. H. Inge, L. L. Hayman,
J. Steinberger, E. M. Urbina, L. J. Ewing, and S. R. Daniels, “Severe
obesity in children and adolescents: Identification, associated health
risks, and treatment approaches: A scientific statement from the american
heart association.,” Circulation, vol. 128, pp. 1689–1712, 10 2013, doi:
1161/CIR.0b013e3182a5cfb3.
Collaborators, “Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries
over 25 years,” New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 377, pp. 13–27,
2017, doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1614362.
R. C. Cervantes and U. M. Palacio, “Estimation of obesity levels
based on computational intelligence,” Informatics in Medicine Unlocked,
vol. 21, p. 100472, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2020.100472.
F. M. Palechor and A. de la Hoz Manotas, “Dataset for estimation
of obesity levels based on eating habits and physical condition in
individuals from colombia, peru and mexico,” Data in Brief, vol. 25,
p. 104344, 8 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2019.104344.
W. Osama, K. R. N, and N. Ghada, “Machine learning for predicting
deposits bank market shares in emerging markets: Evidence from
egypt,” REVISTA GESTÃO & TECNOLOGIA, pp. 473–492, 2023, doi:
20397/2177-6652/2023.v23i4.2729.
M. H. L. Cunha and H. S. Lara, “Machine learning as a way to have more
accuracy when defining milk quality classification,” Seven Congress, 8
, doi: 10.56238/homeinternationalanais-069.
E. De-La-Hoz-Correa, F. E. Mendoza-Palechor, A. De-La-Hoz-Manotas,
R. C. Morales-Ortega, and S. H. B. Adriana, “Obesity level estimation
software based on decision trees,” Journal of Computer Science, vol. 15,
pp. 67–77, 1 2019, doi: 10.3844/jcssp.2019.67.77.
F. Ferdowsy, K. S. A. Rahi, M. I. Jabiullah, and M. T. Habib,
“A machine learning approach for obesity risk prediction,” Current
Research in Behavioral Sciences, vol. 2, p. 100053, 11 2021, doi:
1016/j.crbeha.2021.100053.
K. Jindal, N. Baliyan, and P. S. Rana, Obesity Prediction Using
Ensemble Machine Learning Approaches, pp. 355–362. 2018, doi:
1007/978-981-10-8636-6_37.
F. H. Yagin, M. Gülü, Y. Gormez, A. Castañeda-Babarro, C. Colak,
G. Greco, F. Fischetti, and S. Cataldi, “Estimation of obesity levels with
a trained neural network approach optimized by the bayesian technique,”
Applied Sciences, vol. 13, p. 3875, 3 2023, doi: 10.3390/app13063875.
D. D. Solomon, S. Khan, S. Garg, G. Gupta, A. Almjally, B. I.
Alabduallah, H. S. Alsagri, M. M. Ibrahim, and A. M. A. Abdallah, “Hybrid
majority voting: Prediction and classification model for obesity,”
Diagnostics, vol. 13, p. 2610, 8 2023, doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152610.
H. G. G. Bag, F. H. Yagin, Y. Gormez, P. P. González, C. Colak,
M. Gülü, G. Badicu, and L. P. Ardigò, “Estimation of obesity levels
through the proposed predictive approach based on physical activity
and nutritional habits,” Diagnostics, vol. 13, p. 2949, 9 2023, doi:
3390/diagnostics13182949.
X. Cheng, S. yu Lin, J. Liu, S. Liu, J. Zhang, P. Nie, B. F. Fuemmeler,
Y. Wang, and H. Xue, “Does physical activity predict obesity—a
machine learning and statistical method-based analysis,” International
Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, vol. 18, p. 3966,
2021, doi: 10.3390/ijerph18083966.
D. Sisodia and D. S. Sisodia, “Prediction of diabetes using classification
algorithms,” Procedia Computer Science, vol. 132, pp. 1578–1585, 2018,
doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2018.05.122.
I. E. Naqa and M. J. Murphy, What Is Machine Learning?, pp. 3–11.
Springer International Publishing, 2015, doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-18305-
_1.
S. Tajjour, S. Garg, S. S. Chandel, and D. Sharma, “A novel hybrid
artificial neural network technique for the early skin cancer diagnosis
using color space conversions of original images,” International Journal
of Imaging Systems and Technology, vol. 33, pp. 276–286, 1 2023, doi:
1002/ima.22784.
M. Arora and I. Bhardwaj, Advances in Information Communication
Technology and Computing, vol. 392. Springer Nature Singapore, 2022,
doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-0619-0.
D. E. Rumelhart and J. L. McClelland, Parallel Distributed Processing.
The MIT Press, 1986, doi: 10.7551/mitpress/5236.001.0001.
S. L. Salzberg, “C4.5: Programs for machine learning by j. ross quinlan.
morgan kaufmann publishers, inc., 1993,” Machine Learning, vol. 16,
pp. 235–240, 9 1994, doi: 10.1007/BF00993309.
G. H. John and P. Langley, “Estimating continuous distributions in
bayesian classifiers,” 2 2013, doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1302.4964.
M. Grandini, E. Bagli, and G. Visani, “Metrics for multi-class classification:
an overview,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2008.05756, 2020, doi:
48550/arXiv.2008.05756.
D. W. Aha, D. Kibler, and M. K. Albert, “Instance-based learning
algorithms,” Machine Learning, vol. 6, pp. 37–66, 1 1991, doi:
1007/BF00153759.
M. Delacre, D. Lakens, and C. Leys, “Why psychologists should by
default use welch’s t-test instead of student’s t-test,” International Review
of Social Psychology, vol. 30, pp. 92–101, 4 2017, doi: 10.5334/irsp.82.