An IoT Ground Station: Mechanics, Control, Antenna, and Reception from a LoRa Satellite Network
Keywords:
IoT ground station, Mechanics, Control, Antenna, LoRa platform, SatellitesAbstract
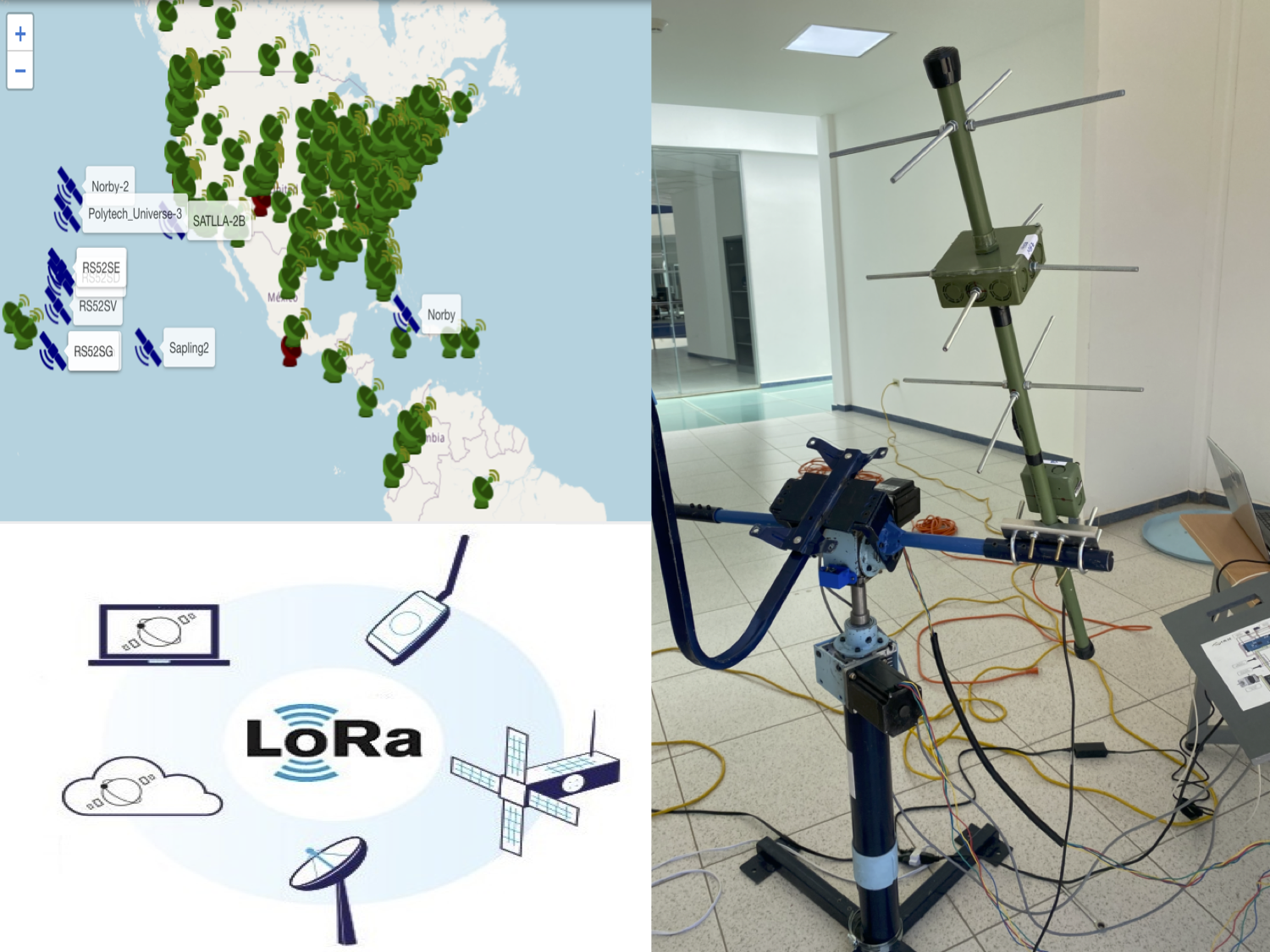
In this article, the design and the integral implementation of a satellite ground station connected to the Internet of Things is presented. The communication system is based on long-range wireless technology, with the objective of receiving telemetry packets from a network of low-arth orbit satellites that transmit at frequencies around 433 MHz. The design covers mechanical design aspects, the control system, the antenna system, and the receiver. The ground station is oriented with respect to the elevation and azimuth coordinates obtained from a web page. This web page contains a console that shows the telemetry packets that have been received, as well as the satellite from which they came. The ground station is a low-cost proposal since commercial ground stations could be purchased at prices much higher than 2 orders of magnitude. All these aspects implied in this easy-to-replicate ground station are especially relevant in educational terms and for amateur radio enthusiasts.
Downloads
References
W. Lan, “Cubesat design specification rev. 13 the cubesat program, cal poly slo cubesat design specification (cds) rev 13 document classification x public domain itar controlled internal only,” 2005.
CalPoly, “6u cubesat design specification rev. 1.0 the cubesat program, cal poly slo 6u cubesat design specification revision 1.0 (cp-6ucds-1.0) document classification x public domain 6u cubesat design specification rev. 1.0 the cubesat program, cal poly slo chang,” 2005.
UCS, “Ucs satellite database,” 1 2023.
H. Ali, A. Ali, M. R. Mughal, L. Reyneri, C. Sansoe, and J. Praks,
“Modular design of rf front end for a nanosatellite communication subsystem tile using low-cost commercial components,” International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, vol. 2019, 2019.
R. N. Vela and S. L. Ayala, Comunicaciones por satélites. Thompson, 1 ed., 2015.
IsisGS, “Isis ground station,” 2023.
M. Elfvelin, “Design and development of the space campus
ground station for small satellites.” urlhttps://www.diva-
portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1646645/FULLTEXT01.pdf, 2022.
J. Orduy-Rodríguez, I. Rodríguez-Barón, and C. Cubillos-Chaparro, “Diseño de una estación terrena sdr para satélites de órbita baja,” Revista Ingeniería, Investigación y Desarrollo, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 41–49, 2019.
J. E. E. Díaz and A. A. R. Hernández, “Methodology to implement a satellite ground university station,” 2015 CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication
Technologies (CHILECON), vol. 2015, 2015.
M. Y. Öztürk and ÇaYavuzyilmaz, “On-board orientation control of a
steerable antenna for ground station tracking on leo satellites,” 2023 10th International Conference on Recent Advances in Air and Space Technologies (RAST), vol. 2023, 2023.
M. Fischer and A. L. Scholtz, “Design of a multi-mission satellite ground station for education and research,” 2010 Second International Confe- rence on Advances in Satellite and Space Communications, vol. 2010, 2010.
TinyGS, “Tinygs,” 2023.
J. E. y. M. L. Espínoza Díaz, Implementación de estación terrena para
seguimiento a picosatélites de órbita LEO. Facultad de Ciencias e
Ingeniería, 2012.
J. L. García García, Diseño de una estación terrena y propuesta de
sistema de telemetría y comando alterno para un satélite de órbita baja.
Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, 2009.
Orbitron, “Orbitron-satellite tracking system,” 2023.
R. S. Burns, Advanced Control Engineering. Butterworth-Heinemann,
ed., 2001.
N. S. Nise, Control Systems Engineering. Wiley, 7 ed., 2010.
A. Modenini and B. Ripani, “A tutorial on the tracking, telemetry, and
command (tt&c) for space missions,” pp. 1–30, 2022.
alijca.space, “How to build a turnstile antenna,” 2023.
X. L. Shan, Yihe and S. Li, “Design and simulation of satellite attitude
controlalgorithm based on pid,” Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
pp. 1–8, 2022.
LILYGO, “Lilygo ttgo lora32 433 mhz v1.6.1,” 2023. [22] ESP32, “Esp32,” 2023.
KN9B, “Kn9b yagi antenna calculator,” 2023.