Techno Economic Assessment of IE3 Electric Motors in the Medium Size Brazilian Industry
Keywords:
Industrial economics, Cost benefit analysis, Induction motors, Electricity, Energy EfficiencyAbstract
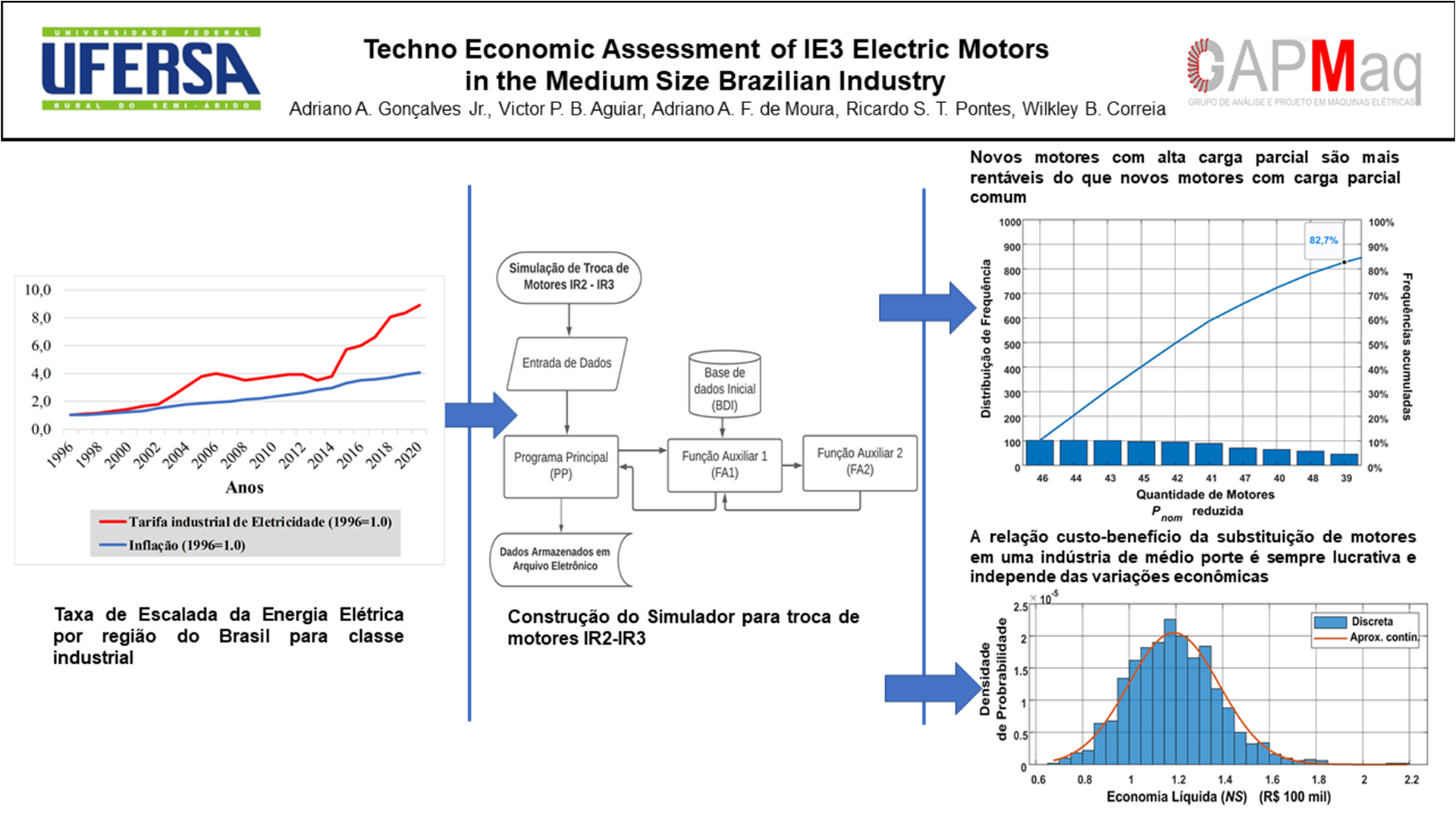
Searching for better efficient energy consumption, actions aimed at induction motors replacement have been consolidated as one of the main investments toward improve energy efficiency. For countries of wide range in electricity tariffs caused by geographic issues, industrial companies operating in different regions have difficulty to define how to direct the investment for energy efficiency actions between your industrial facilities. Thus, this paper aims to present how to direct the financial resources to perform the electric motors replacement to only one industrial facility from techno economic analysis through simulation of different scenarios for each case. Three regions of Brazil named Southeast, Midwest and Northeast were chosen for this analysis due to the highlight in their electricity tariffs characteristics. Regional aspects were taken into account, e.g., electricity escalation rate and electricity tariff as well as technical issues related to how limit the load of the new motors with reduced rated power after replacement. The results are promising because the cost-effectiveness of motors replacement in a medium-size industrial company always profitable regardless economic variations. The higher net savings defines what facilities in different regions of Brazil will have its motors replaced. So, the cost-effectiveness of motors replacement increases while electricity escalation rate, tariff and motor partial load increase.
Downloads
References
Governo Federal do Brasil. Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica, Superintendência de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento e Eficiência Energética. (2015, October). Chamada nº 002/2015, Projeto Prioritário de Eficiência Energética, Incentivo à Substituição de Motores Elétricos: Promovendo a Eficiência Energética no Segmento de Força Motriz. [Online]. Available: https://www.aneel.gov.br/programa-eficiencia-energetica.pdf
Governo Federal do Brasil. Ministério de Minas e Energia, Gabinete do Ministro. (2017, June 29). Portaria. Interministerial. n. 1, Programa de Metas para Motores Elétricos Trifásicos de Indução Rotor Gaiola de Esquilo. [Online]. Available: https://www.gov.br/mme/pt-br/assuntos/conselhos-e-comites/cgiee/arquivos/portarias/2017-portaria-interministerial-mme-mctic-mdic-n_1-2017-motores-eletricos-trifasicos.pdf
Máquinas elétricas girantes. Parte 1: Motores de indução trifásicos - Requisitos, ABNT NBR 17094-1, ABNT, Rio de Janeiro, 2018.
C. T. C. Andrade, “Uma Abordagem Determinística com Análise de Incerteza para a Viabilidade de Programas de Eficiência Energética,” Ph.D. thesis, Dept. Electric Eng., Ceará Fed. Univ., Fortaleza, Brasil, 2017.
S. Sorrell. “The Rebound Effect: An Assessment of the Evidence for Economy-wide Energy Savings from Improved Energy Efficiency,” UK Energy Research Centre. London, U.K. Oct., 2007. [Online] Available: https://www.ukerc.ac.uk/publications/the-rebound-effect-and-assessment-of-the-evidence-for-economy-wide-energy-savings-from-improved-energy-efficiency/.
S. K. Fuller and S. R. Petersen. “Life-Cycle Costing Manual for the Federal Energy Management Program,” National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Gaithersburg, MD, USA, Feb. 1996. [Online]. Available: https://www.nist.gov/publications/life-cycle-costing-manual-federal-energy-management-program-nist-handbook-135-1995.
K. C. D. Lima et al., Santo André, SP, Brasil. Avaliação Técnico-Econômica da Troca de Motores Industriais pela Análise do Carregamento e Cálculo da Economia Líquida em uma Indústria Salineira. Presented at VII Simpósio Brasileiro de Sistemas Elétricos (SBSE). [Online]. Available: https://eventos.galoa.com.br/sbse-2020
C. T. C. Andrade, R. S. T. Pontes, “Economic analysis of Brazilian policies for energy efficient electric motors,” Energy Policy, vol. 106, no. 7, pp. 315–325, Jul. 2017, 10.11016/j.enpol.2017.03.029.
G. A. McCoy and J. G. Douglass. “Premium Efficiency Motor Selection and Application Guide – A Handbook for Industry,” US Department of Energy. Washington, DC, USA, Feb., 2014. [Online]. Available: https://www.energy.gov/eere/amo/downloads/premium-efficiency-motor-selection-and-application-guide-handbook-industry.
I. Boldea and S. A. Nasar, “Steady-State Equivalent Circuit and Performance” in The Induction Machine Handbook, 2nd ed. Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press, 2010, ch. 7.
V. P. B. Aguiar, “Avaliação técnico-econômica do aumento do rendimento em motores de indução trifásicos de baixa potência após rebobinagem,” Ph.D. thesis, Dept. Electric Eng., Ceará Fed. Univ., Fortaleza, Brasil, 2017.
V. P. B. Aguiar, R. S. T. Pontes, and F. J. T. E. Ferreira, “Technical and Economic Evaluation of Efficiency Improvement after Rewinding in Low-Power Induction Motors: A Brazilian Case,” Energies, vol. 11, no. 7, Jul. 2018, Art. no. 1701, 10.3390/en11071701.
X. Yu, J. M. Cruz, and J. C. Crittenden, “Regional energy rebound effect: The impact of economy-wide and sector level energy efficiency improvement in Georgia, USA,” Energy Policy., vol. 87, no. 12, pp. 250-259, Dez. 2015.
Manual para Elaboração do Programa de Eficiência Energética. Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica (ANEEL). Brasília, Brazil. 2008. [Online]. Available: https://www.aneel.gov.br/documents/656831/14944470/Manual+de+Elaboração+do+PEE+2008.pdf
Relatórios de Consumo e Receita de Distribuição. Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica (ANEEL). Brasília, Brazil. [Online]. Available: https://www.aneel.gov.br/relatorios-de-consumo-e-receita.
Ipeadata. Instituto de Pesquisa Econômica e Aplicada (IPEA). Brasília, Brazil. [Online]. Available: https://www.ipeadata.gov.br.
Catálogo eletrônico WEG W22. WEG Motores. Jaraguá do Sul, Brazil. [Online]. Available: https://www.weg.net.catalog/weg/BR/pt/Motores-Elétricos/c/BR_MT.