Conservative Power Theory for Harmonic Voltage Responsibility Assignment
Keywords:
Conservative power theory, harmonic distortion, power quality, sharing of responsibilityAbstract
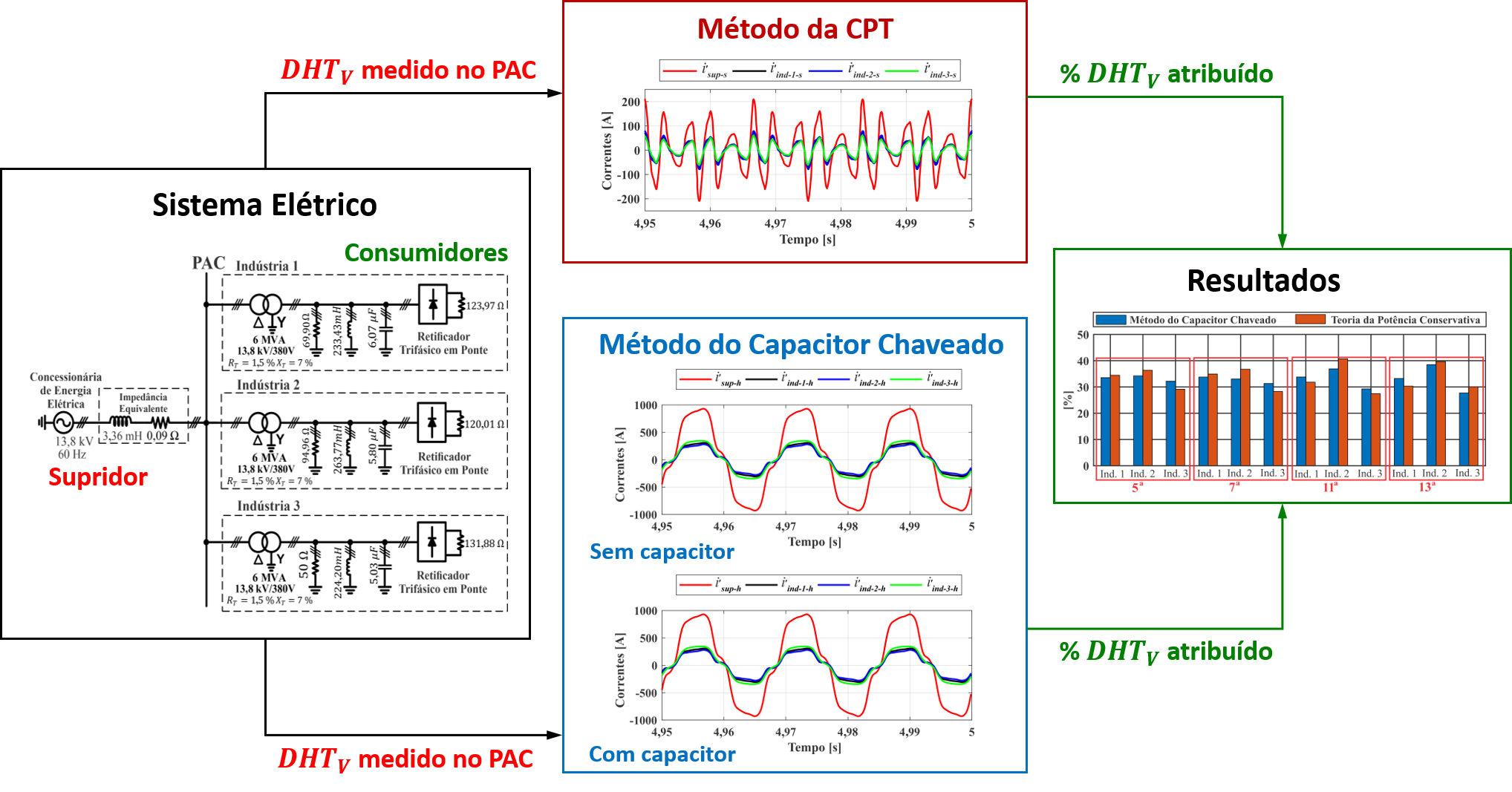
Discussions on the different methods for sharing responsibilities regarding harmonic distortions in power grids have received wide attention in the area of power quality. This paper proposes a methodology based on Conservative Power Theory (CPT) for responsibility assignment due to the harmonic voltage distortions present at the point of common coupling. First, a theoretical basis for analyzing the orthogonal current decomposition of CPT under non-sinusoidal conditions is presented. Next, using the frequency domain, a methodology is introduced to separate the contributions of the harmonic voltage distortions in the CPT's orthogonal currents. To illustrate the application of the proposed methodology, it is simulated a real large-scale electrical system composed of an energy utility and three industrial plants connected to the same common coupling point. Finally, the results obtained are compared to other method showing the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Downloads
References
A. E. Emanuel et al., “Voltage distortion in distribution feeders with nonlinear loads,” IEEE Trans Power Delivery, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 79-87, Jan. 1994, DOI: 10.1109/61.277682.
N. R. Watson, T. L. Scott and S. J. J. Hirsch, “Implications for distribution networks of high penetration of compact fluorescent lamps,” IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 1521-1528, July 2009, DOI: 10.1109/TPWRD.2009.2014036.
M. H. J. Bollen et al., “Power quality concerns in implementing smart distribution-grid applications,” IEEE Trans. on Smart Grid, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 391-399, Jan. 2017, DOI: 10.1109/TSG.2016.2596788.
A. Kalair, N. Abas, A. R. Kalair, Z. Saleem, N. Khan, “Review of harmonic analysis, modeling and mitigation techniques”, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 78, pp. 1152-1187, 2017.
IEEE – Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Recommended Practice and Requirements for Harmonic Control in Electric Power Systems, IEEE Standard 519-2014 (Revision of IEEE Std 519-1992).
International Electrotechnical Commission, Electromagnetic Compatibility, (EMC). Part 3: Limits – Section 6: Assessment of Emission Limits for Distorting Loads in MV and HV Power Systems ‐ Basic EMC publication, IEC 61000‐3‐6, 2008.
EN 50160. Voltage characteristics of electricity supplied by public distribution networks, Technical report, EN 50160, 2001.
A. C. Santos, J. C. Oliveira, I. N. Santos, “A comparative analysis between methodologies for responsibility assignment on harmonic distortions”, Renewable Energy and Power Quality Journal, vol. 1(13), pp. 305-310, 2015.
M. Shojaie, H. Mokhtari, “A method for determination of harmonics responsibilities at the point of common coupling using data correlation analysis”, IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, vol. 8(1), pp. 142-150, 2014.
T. Tanak, H. Akagi, “A new method of harmonic power detection based on the instantaneous active power in three-phase circuits”, IEEE Trans. Power Deliver, vol. 10(4), pp. 1737-1742, 1995.
K. Srinivasan, “On separating customer and supply side harmonic contributions”, IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, vol. 11(2), pp. 1003-1012, 1996.
W. Xu, Y. Liu, “A method to determine customer harmonic contributions for incentive‐based harmonic control applications”, IEEE Power Engineering Society Summer Meeting. 1999.
I. N. Santos, J. C. Oliveira, J. R. Macedo, “Modified superposition method as a new approach to assigning responsibilities on harmonics distortions”, Controle & Automação, vol. 23(6), pp. 782‐796, 2012.
F. M. Fernandez, P.S. C. Nair, “Method for separation of customer and utility contributions of harmonics at point of common coupling”, IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, vol. 7(4), pp. 374-381, 2013.
L. Cristaldi, A. Ferrero, “Harmonic power flow analysis for the measurement of the electric power quality”, IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., vol. 44(3), pp. 683-685, 1995.
P. H. Swart, M. J. Case, J. D. V. Wyk, “On techniques for localization of sources producing distortion in three-phase networks”, European Transaction on Electrical Power, vol. 6(6), pp. 391-396, 1996.
K. Srinivasan, R. Jutras, “Conforming and non-conforming current for attributing steady state power quality problems”, IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, vol. 13(1), pp. 212-217, 1998.
W. Xu, Y. Liu, “A method for determining customer and utility harmonic contributions at the point of common coupling”, IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, vol. 15(2), pp. 804‐811, 2000.
J. C. Das, “Passive filters - potentialities and limitations”, IEEE Trans. Industry Applications, vol. 40(1), pp. 232-241, 2004.
A. C. Santos, I. N. Santos, J. C. Oliveira, “Capacitor switching methodology for responsibility sharing of harmonic voltage distortions”, Electrical Energy Systems, vol. 29(12), pp. e12135, 2019.
N. Locci, C. Muscas, S. Sulis, “Detrimental effects of capacitors in distribution networks in the presence of harmonic pollution”, IEEE Transaction on Power Delivery. vol. 22(1), pp. 311-315, 2007.
P. Tenti, H. K. M. Paredes and P. Mattavelli, "Conservative Power Theory, a Framework to Approach Control and Accountability Issues in Smart Microgrids," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 664-673, March 2011, doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2010.2093153.
P. Tenti, H. K. M. Paredes, F. P. Marafao and P. Mattavelli, "Accountability in Smart Microgrids Based on Conservative Power Theory," in IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, vol. 60, no. 9, pp. 3058-3069, Sept. 2011, doi: 10.1109/TIM.2011.2162351.
W. A. Souza, E. V. Liberado, L. C. P. Silva, F. P. Marafão, H. K. Morales-Paredes, “Load analyzer using conservative power theory”, Przeglad Elektrotechniczny. vol. 89(12) pp. 1-6, 2013.
A. C. Moreira, W. A. de Souza, B. R. P. Conrado, et al. “Disturbing Load Classification Based on the Grey Relational Analysis Method and Load Performance Index”. J Control Autom Electr Syst 31, 141–152 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-019-00511-9.
F. P. Marafão, D. I. Brandão, F. A. S. Gonçalves, et al. “Decoupled Reference Generator for Shunt Active Filters Using the Conservative Power Theory”. J Control Autom Electr Syst 24, 522–534 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-013-0043-0.
C. Burgos-Mellado et al., "Experimental Evaluation of a CPT-Based Four-Leg Active Power Compensator for Distributed Generation," in IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 747-759, June 2017, doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2016.2633064..
F. P. Marafão, D. I. Brandão, A. Costabeber, H. K. Morales Paredes, “Multi-task control strategy for grid-tied inverters based on conservative power theory”, IET Renewable Power Generation, 2015, 9, (2), p. 154-165, DOI: 10.1049/iet-rpg.2014.0065.
J. P. Bonaldo, H. K. Morales Paredes and J. A. Pomilio, "Control of Single-Phase Power Converters Connected to Low-Voltage Distorted Power Systems With Variable Compensation Objectives," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 2039-2052, March 2016, doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2015.2440211.
H. K. M. Paredes, D. T. Rodrigues, J. C. Cebrian and J. P. Bonaldo, "CPT-Based Multi-Objective Strategy for Power Quality Enhancement in Three-Phase Three-Wire Systems Under Distorted and Unbalanced Voltage Conditions," in IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 53078-53095, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3069832.
H. K. Morales-Paredes, “Conservative Power Theory: A new approach to cooperative control of power conditioners and considerations regarding to responsibility assignment”, PhD thesis , FEEC. UNICAMP, SP, 2011.