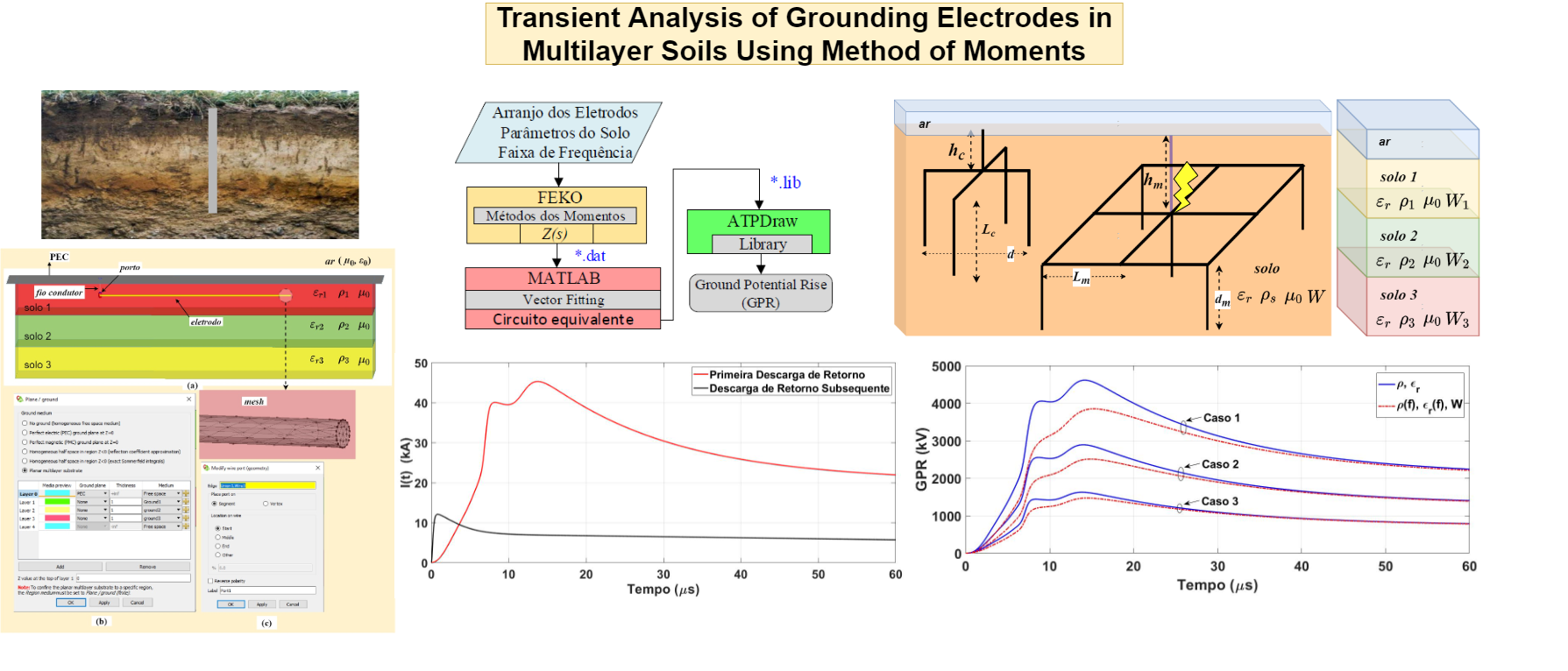
Transient Analysis of Grounding Electrodes in Multilayer Soils Using Method of Moments
Keywords:
lightning, grounding electrodes, method of moments, Electromagnetic transientsAbstract
Grounding electrodes are expected to provide a low-impedance path for faults and lightning transient currents and protect the safety of electrical equipment and nearby people against dangerous induced potentials. In this context, a precise model of the grounding electrodes is needed to represent a certain electrode arrangement buried in stratified soil. This paper computes the grounding impedances of different grounding systems buried in three different soil configurations (homogeneous, 2-layer and 3-layer soil) modeled by its frequency-dependent electrical parameters. A simulation model using a commercial full-wave electromagnetic software FEKO to compute the grounding impedances is presented. Method of Moments(MoM), a frequency-domain numerical method, is employed to compute the grounding impedance in a frequency range of100 Hz to 5 MHz. Next, the developed ground potential rise(GPR) generated by two types of lightning currents (first and subsequent return strokes) injected into these grounding systems is computed. Time-domain GPR of each grounding system is also determined using the Vector Fitting (VF) technique combined with the ATP-software. Results show that GPR waveform is reduced when frequency-dependent soils are employed. This reduction is more pronounced in homogeneous and in 2-layersoils of high and moderated resistivity whereas the 3-layer soil has a minor impact due to the lower soil resistivity
Downloads
References
L. Grcev, “Modeling of grounding electrodes under lightning currents,”
IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, vol. 51, no. 3
PART 1, pp. 559–571, 2009.
A. De Conti and R. Alipio, “Single-port equivalent circuit representation
of grounding systems based on impedance fitting,” IEEE Transactions
on Electromagnetic Compatibility, vol. 61, no. 5, pp. 1683–1685, 2019.
R. S. Al´ıpio, M. M. Afonso, T. A. S. d. Oliveira, and M. A. d. O.
Schroeder, “Modelagem de aterramentos el´etricos para fenˆomenos de
alta frequˆencia e comparac¸ ˜ao com resultados experimentais,” Sba:
Controle & Automac¸ ˜ao Sociedade Brasileira de Automatica, vol. 22,
no. 1, pp. 89–102, 2011.
B. Salarieh, H. J. De Silva, and B. Kordi, “Electromagnetic
transient modeling of grounding electrodes buried in frequency
dependent soil with variable water content,” Electric Power
Systems Research, vol. 189, p. 106595, 2020. [Online]. Available:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378779620303990
R. Alipio and S. Visacro, “Frequency dependence of soil parameters:
Effect on the lightning response of grounding electrodes,” IEEE Transactions
on Electromagnetic Compatibility, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 132–139, 2013.
Z. G. Datsios and P. N. Mikropoulos, “Characterization of the frequency
dependence of the electrical properties of sandy soil with variable grain
size and water content,” IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical
Insulation, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 904–912, 2019.
A. E. Ruehli, G. Antonini, and L. Jiang, Circuit-oriented electromagnetic
modeling using the PEEC techniques. Wiley Online Library, 2017.
F. Pereira, M. Afonso, M. Schroeder, and T. Oliveira, “Espalhamento
eletromagn´etico: An´alise de estruturas condutoras via m´etodo de momentos,”
CEP, vol. 30510, p. 000.
Altair, User Manual for FEKO 2019. Altair, 2019.
R. F. Harrington, Field computation by moment methods. Wiley-IEEE Press, 1993.
B. Gustavsen and A. Semlyen, “Rational approximation of frequency
domain responses by vector fitting,” IEEE Transactions on Power
Delivery, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 1052–1061, 1999.
E. Ba˜nuelos-Cabral, J. Guti´errez-Robles, J. Garc´ıa-S´anchez, J. Sotelo-
Casta˜n´on, and V. Galv´an-S´anchez, “Accuracy enhancement of the jmarti
model by using real poles through vector fitting,” Electrical Engineering,
vol. 101, no. 2, pp. 635–646, 2019.
G. Antonini, “Spice equivalent circuits of frequency-domain responses,”
IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, vol. 45, no. 3, pp.
–512, 2003.
F. H. Silveira, A. De Conti, and S. Visacro, “Lightning overvoltage
due to first strokes considering a realistic current representation,” IEEE
Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 929–
, 2010.
L. D. Grcev, A. Kuhar, V. Arnautovski-Toseva, and B. Markovski,
“Evaluation of high-frequency circuit models for horizontal and vertical
grounding electrodes,” IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, vol. 33,
no. 6, pp. 3065–3074, 2018.
L. Grcev and M. Heimbach, “Frequency-dependent and transient characteristics
of substation grounding systems,” IEEE Transactions on Power
Delivery, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 172–178, 1997.
B. Salarieh, J. De Silva, and B. Kordi, “High frequency response of
grounding electrodes: effect of soil dielectric constant,” IET Generation,
Transmission & Distribution, 2020.