Performance Evaluation of Data Transactions in Blockchain
Keywords:
Blockchain, Architectures, Smart contracts, Performance analysis, ApplicationAbstract
Blockchain is an emerging technology, with a decentralized infrastructure avoiding third party dependency. Smart
contracts are one of the features of Ethereum blockchain, capable of running distributed applications in unreliable
environments, enabling process automation and being one of the most sought technologies due to the high
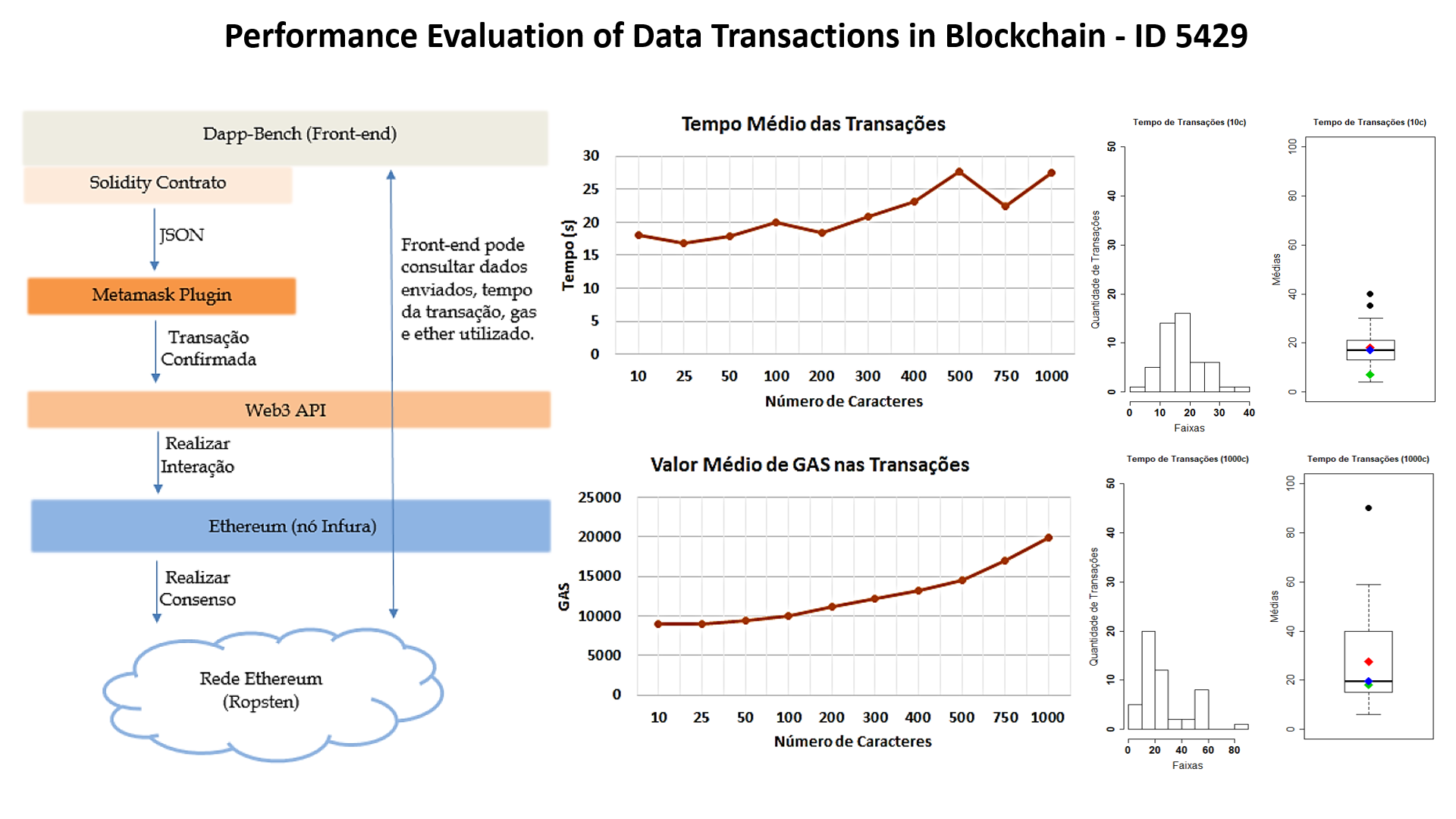
customization added to transactions. However, little is known about predicting the cost and execution time behavior of blockchain-based system transactions. This work aims to evaluate the performance of an Ethereum network through an application designed to analyze the cost and time of transactions that store characters in the blockchain. To meet the proposed objective, we designed an application for performing transactions with data inclusion and query on a blockchain, collecting time and cost data. As main conclusions of this work we have: the Ethereum platform proved to be inconstant in relation to the processing time of transactions on the blockchain and the application developed based on blockchain can provide a mechanism to evaluate text-type operations on Ethereum network.
Downloads
References
A. Bosu, A. Iqbal, R. Shahriyar, and P. Chakraborty, “Understanding the motivations, challenges and needs of blockchain software developers: A survey,” Empirical Software Engineering, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 2636–2673, 2019.
D. Macrinici, C. Cartofeanu, and S. Gao, “Smart contract applications within blockchain technology: A systematic mapping study,” Telematics and Informatics, vol. 35, no. 8, pp. 2337 – 2354, 2018.
S. Huh, S. Cho, and S. Kim, “Managing iot devices using blockchain platform,” in 2017 19th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), pp. 464–467, Feb 2017.
K. Korpela, J. Hallikas, and T. Dahlberg, “Digital supply chain transformation toward blockchain integration,” in 50th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), jan 2017.
A. Azaria, A. Ekblaw, T. Vieira, and A. Lippman, “Medrec: Using blockchain for medical data access and permission management,” in 2016 2nd International Conference on Open and Big Data (OBD), pp. 25–30, Aug 2016.
P. Thakkar, S. Nathan, and B. Viswanathan, “Performance benchmarking and optimizing hyperledger fabric blockchain platform,” in 2018 IEEE 26th International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis, and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems (MASCOTS), pp. 264–276, Sep. 2018.
M. Jakobsson and A. Juels, Proofs of Work and Bread Pudding Protocols (Extended Abstract), pp. 258–272. Boston, MA: Springer US, 1999.
M. Nofer, P. Gomber, O. Hinz, and D. Schiereck, “Blockchain,” Business & Information Systems Engineering, vol. 59, pp. 183–187, Jun 2017.
N. Rifi, E. Rachkidi, N. Agoulmine, and N. C. Taher, “Towards using blockchain technology for ehealth data access management,” in 2017Fourth International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME), pp. 1–4, Oct 2017.
G. Wood, “Ethereum: A secure decentralised generalised transaction ledger - v. 3e36772,” 2019.
N. Szabo, “Smart contracts.” http://bit.ly/2Yc9vjb, 1994. Online; acces-sed Oct-2019.
M. Alharby and A. van Moorsel, “Blockchain-based smart contracts: A systematic mapping study,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.06372, 2017.
K. Christidis and M. Devetsikiotis, “Blockchains and smart contracts for the internet of things,” IEEE Access, vol. 4, pp. 2292–2303, 2016.
K. Delmolino, M. Arnett, A. Kosba, A. Miller, and E. Shi, “Step by step towards creating a safe smart contract: Lessons and insights from a cryptocurrency lab,” in Financial Cryptography and Data Security (J. Clark, S. Meiklejohn, P. Y. Ryan, D. Wallach, M. Brenner, andK. Rohloff, eds.), (Berlin, Heidelberg), pp. 79–94, Springer BerlinHeidelberg, 2016.
A. Aldweesh, M. Alharby, E. Solaiman, and A. van Moorsel, “Performance benchmarking of smart contracts to assess miner incentives in ethereum,” in 2018 14th European Dependable Computing Conference (EDCC), pp. 144–149, Sep. 2018.
Z. Dong, E. Zheng, Y. Choon, and A. Y. Zomaya, “Dagbench: Aperformance evaluation framework for dag distributed ledgers,” in 2019 IEEE 12th International Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD), pp. 264–271, July 2019.
A. Meeuw, S. Schopfer, and F. Wortmann, “Experimental bandwidth benchmarking for p2p markets in blockchain managed microgrids,” Energy Procedia, vol. 159, pp. 370 – 375, 2019. Renewable EnergyIntegration with Mini/Microgrid.
E. F. Coutinho, D. J. H. Maia, W. L. B. Bezerra, and A. W. dos Santos Abreu, “Avaliando o custo de contratos inteligentes em aplicações blockchain por meio de ambientes de simulação,” in Anais do II Workshop em Modelagem e Simulação de Sistemas Intensivos emSoftware, (Porto Alegre, RS, Brasil), pp. 56–65, SBC, 2020.
Y.Majuri, “Simplyexplained:Smartcontracts.” https://medium.com/@yakko.majuri/blockchain-definition-of-the-week-smart-contracts-1fbef0d25abf, 2018. Online; accessed Oct-2019.
X. Xu, I. Weber, and M. Staples, Blockchain in Software Architecture, pp. 83–92. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019.
S. Chen, J. Zhang, R. Shi, J. Yan, and Q. Ke, “A comparative testing on performance of blockchain and relational database: Foundation for applying smart technology into current business systems,” in Distributed, Ambient and Pervasive Interactions: Understanding Humans (N. Streitzand S. Konomi, eds.), (Cham), pp. 21–34, Springer International Publishing, 2018.