A Technical and Economic Criteria Comparison on Demand Side Management with Multi-Level Optimization Model
Keywords:
Demand Side Management, Smart Grids, Demand Response, Multilevel Optimization, Genetic Algorithm, Indirect controlAbstract
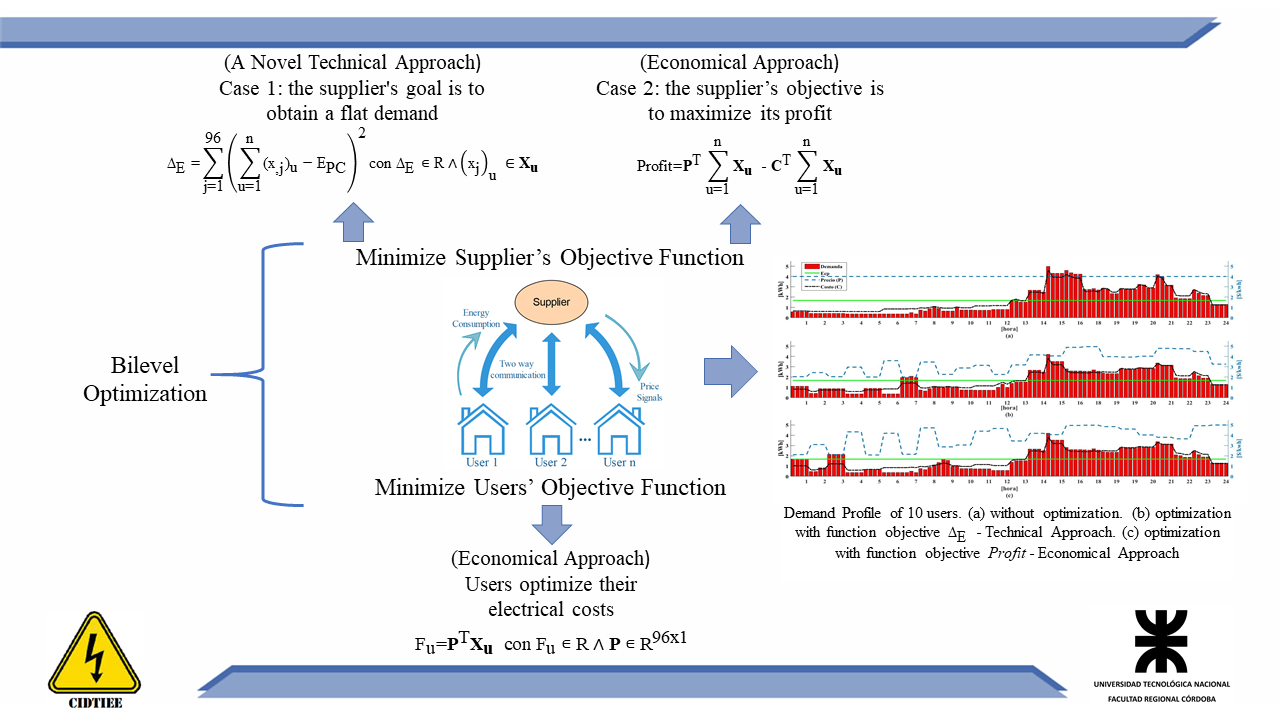
One-level optimization methods have been proposed to optimize the load profile of a single user or a cluster of users in the smart grids. In this work, two two-level optimization methods are studied, one considering technical requirements and other considering economic criteria. In the upper level, the supplier optimizes it objective function. Meanwhile, at the lower level, users optimize their electrical costs. The proposed methods are based on genetic algorithm methods. In this sense, an indirect control is established in which users react to a price signal. Simulations results illustrate that both cases improve the demand profile and increase the retailer profit. However, when the supplier tries to maximize the profit, some users receive benefits in detriment of others, concluding that the technical approach is preferable than the economical one.
Downloads
References
M. Subasic, “Advanced state estimation in distribution systems,” Ph.D, Politécnico de Milan, Italia, 2015.
S. N. Bragagnolo, J. C. Vaschetti, F. Magnago, and J. C. Gomez Targarona, “Gestión de la demanda en las redes inteligentes, perspectiva y control desde el usuario y la distribuidora,” Información tecnológica, vol. 31, no. 3, 2020.
A. R. Jordehi, “Optimisation of demand response in electric power systems, a review,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 103, pp. 308–319, 2019.
F. Gardumi, “A multi-dimensional approach to the modelling of power plant flexibility,” Ph.D, Politécnico de Milan, Italy, 2016.
J. G. Kassakian et al., “The future of the electric grid: An interdisciplinary MIT study,” URL http://energy. mit. edu/research/future-electric-grid/.[Accessed 16 Aug 2018], 2011.
A. Molderink, V. Bakker, M. G. Bosman, J. L. Hurink, and G. J. Smit, “Management and control of domestic smart grid technology,” IEEE transactions on Smart Grid, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 109–119, 2010.
S. Yilmaz, J. Chambers, and M. K. Patel, “Comparison of clustering approaches for domestic electricity load profile characterisation-Implications for demand side management,” Energy, vol. 180, pp. 665–677, 2019.
P. Siano, “Demand response and smart grids—A survey,” Renewable and sustainable energy reviews, vol. 30, pp. 461–478, 2014.
C. H. Antunes, M. J. Alves, and B. Ecer, “Bilevel optimization to deal with demand response in power grids: models, methods and challenges,” TOP, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 814–842, 2020.
P. Carrasqueira, M. J. Alves, and C. H. Antunes, “Bi-level particle swarm optimization and evolutionary algorithm approaches for residential demand response with different user profiles,” Information Sciences, vol. 418, pp. 405–420, 2017.
A. Kovács, “Bilevel programming approach to demand response management with day-ahead tariff,” Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 1632–1643, 2019.
S. Janocha, S. Baum, and I. Stadler, “Cost minimization by optimization of electricity generation and demand side management,” International Energy and Sustainability Conference (IESC), pp. 1–7, 2016.
C. Li, D. Srinivasan, and T. Reindl, “Real-time scheduling of time-shiftable loads in smart grid with dynamic pricing and photovoltaic power generation,” IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies-Asia (ISGT ASIA), pp. 1–6, 2015.
N. Javaid, I. Khan, M. Ullah, A. Mahmood, and M. U. Farooq, “A survey of home energy management systems in future smart grid communications,” Eighth International Conference on Broadband and Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications, pp. 459–464, 2013.
A. Anvari-Moghaddam, H. Monsef, A. Rahimi-Kian, J. M. Guerrero, and J. C. Vasquez, “Optimized energy management of a single-house residential micro-grid with automated demand response,” IEEE Eindhoven PowerTech, pp. 1–6, 2015.
H. Karami, M. J. Sanjari, S. H. Hosseinian, and G. B. Gharehpetian, “An optimal dispatch algorithm for managing residential distributed energy resources,” IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 2360–2367, 2014.
T. Logenthiran, D. Srinivasan, and T. Z. Shun, “Demand side management in smart grid using heuristic optimization,” IEEE transactions on smart grid, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 1244–1252, 2012.
H.-T. Yang, C.-T. Yang, C.-C. Tsai, G.-J. Chen, and S.-Y. Chen, “Improved PSO based home energy management systems integrated with demand response in a smart grid,” IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), pp. 275–282. 2015.
I. O. Essiet, Y. Sun, and Z. Wang, “Optimized energy consumption model for smart home using improved differential evolution algorithm,” Energy, vol. 172, pp. 354–365, 2019.
D. Bertineti, L. Canha, A. Medeiros, R. de Azevedo, and B. da Silva, “Heuristic Scheduling Algorithm for Load Shift DSM Strategy in Smart Grids and IoT Scenarios,” IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference-Latin America (ISGT Latin America), pp. 1–6. 2019.
A. R. Vidal, L. A. Jacobs, and L. S. Batista, “An evolutionary approach for the demand side management optimization in smart grid,” in IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence Applications in Smart Grid (CIASG), 2014, pp. 1–7.
N. D. Rahate and N. Kinhekar, “Demand side management for household equipment’s,” International Conference on Information, Communication, Instrumentation and Control (ICICIC), pp. 1–5. 2017..
I. Gupta, G. Anandini, and M. Gupta, “An hour wise device scheduling approach for demand side management in smart grid using particle swarm optimization,” National Power Systems Conference (NPSC), pp. 1–6. 2016.
A. C. Batista and L. S. Batista, “Demand side management using a multi-criteria ϵ-constraint based exact approach,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 99, pp. 180–192, 2018.
S. N. Bragagnolo, J. C. Vaschetti, F. Magnago, and J. C. Gomez Targarona, “Gestión de la Demanda en las Redes Inteligentes, Perspectiva y Control desde el Usuario y la Distribuidora,” presented at the Congreso Internacional de Distribución Eléctrica (CIDEL 2018), Buenos Aires, Argentina, Sep. 2018.
M. Besançon, M. F. Anjos, L. Brotcorne, and J. A. Gómez-Herrera, “A Bilevel Approach for Optimal Price-Setting of Time-and-Level-of-Use Tariffs,” IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 5462–5465, 2020.
F.-L. Meng and X.-J. Zeng, “An optimal real-time pricing for demand-side management: A Stackelberg game and genetic algorithm approach,” International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1703–1710. 2014.
F.-L. Meng and X.-J. Zeng, “A bilevel optimization approach to demand response management for the smart grid,” IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), pp. 287–294. 2016.
S. Belhaiza and U. Baroudi, “A game theoretic model for smart grids demand management,” IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 1386–1393, 2014.
G. Huang, J. Yang, and C. Wei, “Cost-Effective and comfort-aware electricity scheduling for home energy management system,” IEEE International Conferences on Big Data and Cloud Computing (BDCloud), Social Computing and Networking (SocialCom), Sustainable Computing and Communications (SustainCom) (BDCloud-SocialCom-SustainCom), pp. 453–460. 2016.
Z. Zhu, S. Lambotharan, W. H. Chin, and Z. Fan, “A game theoretic optimization framework for home demand management incorporating local energy resources,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 353–362, 2015.
D. Bian, M. Pipattanasomporn, and S. Rahman, “A human expert-based approach to electrical peak demand management,” IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, vol. 30, no. 3, pp. 1119–1127, 2015.
D. H. Celiz, M. Figueroa Etchecopar, M. Piumetto, S. N. Bragagnolo, J. C. Vaschetti, and J. C. Gomez Targarona, “Estudio y Análisis para Definir Políticas que Modifiquen las Conductas de Consumo en Usuarios Domiciliarios Monofásicos,” presented at the IV Congreso Argentino de Ingeniería – X Congreso Argentino de Enseñanza de la Ingeniería (CADI-CAEDI 2018), Córdoba, Argentina, Sep. 2018.
“EPEC.” https://www.epec.com.ar/ (accessed Jun. 29, 2020).