Indoor Navigation Technologies Based on RFID Systems to Assist Visually Impaired People: A Review and a Proposal
Keywords:
Electronics technology, Indoor environments, Indoor location, Indoor navigation, Orientation, Radiofrequency communication, RFID, Visually impaired peopleAbstract
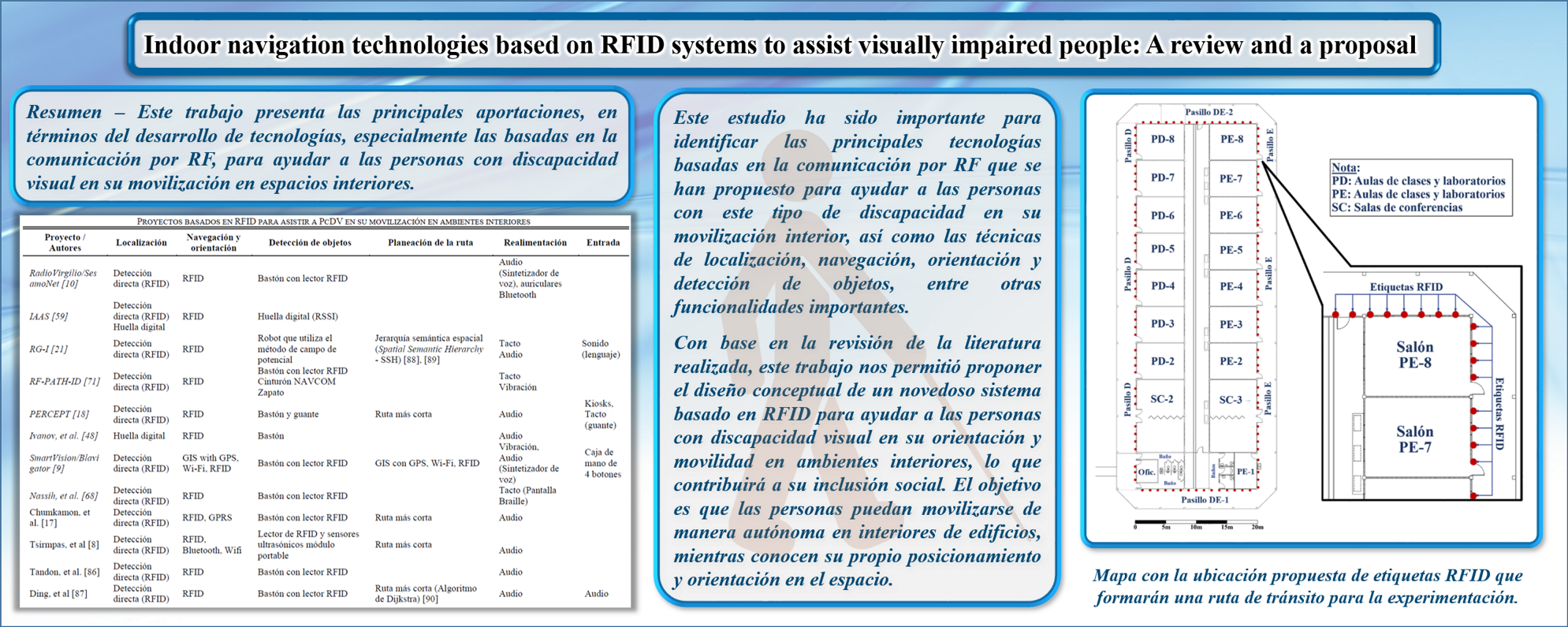
This paper presents a study of the main contributions, in terms of the development of electronics and RFID technologies, to assist people with visual disabilities in their mobilization in indoor spaces. The main aspects taken into consideration when designing an assistive system for people with visual impairments for planning and execution of a movement from one place to another and/or for exploration of a site of interest autonomously are included. This study is important to identify the main technologies based on circuits and systems, electronics, ICT, and RF communication that have been proposed to help people with this type of disability in their indoor mobilization, as well as the techniques of location, navigation, orientation, and detection of objects, among other important functionalities for this type of systems. This work allowed us to propose the conceptual design of a novel system based on RFID and electronics technologies to help visually impaired people in their navigation in indoor environments, which will contribute to their social inclusion.
Downloads
References
D. García Moreno, “Diseño de sistemas de orientación espacial: wayfinding”, in Acces. Univ. y Dis. para Todos. Arq. y Urbanismo. Fund. ONCE y Fund. Arquit. COAM, España, 2011, pp. 36-57.
P. López Pereda, “Diseño arquitectónico para todas las personas”, in Acces. Univ. y Dis. para Todos. Arq. y Urbanismo. Fund. ONCE y Fund. Arquit. COAM, España, 2011, pp. 82-105.
ONCE, "Desplazamiento por espacios interiores", in Discapacidad visual y autonomía personal: enfoque práctico de la rehabilitación, 1st ed., España, 2011, pp. 516-531.
A. Pereira, N. Nunes, D. Vieira, N. Costa., H. Fernandes and J. Barroso, “Blind Guide: An ultrasound sensor-based body area network for guiding blind people.” Procedia Comput. Sci., 67, pp.403-408, 2015.
M. Bousbia-Salah, M. Bettayeb and M. Larbi, “A navigation aid for blind people.” J. Intell. & Robot. Sys., vol. 64, no. 3-4, pp.387-400, Dec. 2011.
I. Ulrich and J. Borenstein.” The GuideCane-applying mobile robot technologies to assist the visually impaired.” IEEE Trans. Systems, Man, and Cybern., Part A: Systems and Humans, vol. 31, no. 2, pp.131-136, 2001.
L. Hakobyan, J. Lumsden, D. O’Sullivan and H. Bartlett. “Mobile assistive technologies for the visually impaired.” Survey of ophthalmology, vol. 58, no. 6, pp.513-528, 2013.
C. Tsirmpas, A. Rompas, O. Fokou and D. Koutsouris. “An indoor navigation system for visually impaired and elderly people based on Radio Frequency Identification (RFID).” Inf. Sci., vol. 320, pp.288-305, 2015.
H. Fernandes, V. Filipe, P. Costa and J. Barroso. “Location based services for the blind supported by RFID technology.” Procedia Comput. Sci., 27, pp.2-8, 2014.
E. D'Atri, C.M. Medaglia, A. Serbanati, U.B. Ceipidor, E. Panizzi and A. D'Atri. “A system to aid blind people in the mobility: A usability test and its results.” In Syst. ICONS'07, pp. 35-35, Abr. 2007.
N. Fallah, I. Apostolopoulos, K. Bekris and E. Folmer. “Indoor human navigation systems: A survey.” Interacting with Comput., vol. 25, no. 1, pp.21-33, 2013.
C. Fischer, K. Muthukrishnan, M. Hazas and H. Gellersen. “Ultrasound-aided pedestrian dead reckoning for indoor navigation.” In Proc. 1st ACM Intl. work. MELT’08 in GPS-less environments, Sep. 2008, pp. 31-36.
T. Höllerer, D. Hallaway, N. Tinna and S. Feiner. “Steps toward accommodating variable position tracking accuracy in a mobile augmented reality system.” In 2nd Intl. Workshop on Artificial Intell. in Mobile Syst. (AIMS’01), Aug. 2001, pp. 31-37.
S. Koide and M. Kato. “3-D human navigation system considering various transition preferences.” In Syst., Man and Cybern., IEEE Intl. Conf., pp. 859-864, 2005.
G. Retscher and M. Thienelt. “NAVIO–a navigation and guidance service for pedestrians.” J. Global Position. Sys, vol. 3, no. 1-2, p.208-217, 2004.
H. Wu, A. Marshall and W. Yu. “Path planning and following algorithms in an indoor navigation model for visually impaired.” In Internet Monitoring and Protection, 2007, pp. 38-38.
S. Chumkamon, P. Tuvaphanthaphiphat and P. Keeratiwintakorn. “A blind navigation system using RFID for indoor environments.” In Electr. Eng./Electron., Comput., Telecommun. and Inf. Technol., 2008, pp. 765-768.
A. Ganz, J. Schafer, S. Gandhi, E. Puleo, C. Wilson and M. Robertson. “PERCEPT indoor navigation system for the blind and visually impaired: architecture and experimentation.” Intl. J. of Telemed. and Appl., pp. 1-12, 2012.
S. Willis and S. Helal. “RFID information grid and wearable computing solution to the problem of wayfinding for the blind user in a campus environment.” In IEEE Intl. Symp. on Wearable Comput., pp. 1-4, Oct, 2005.
Y. Duroc and S. Tedjini, “La RFID une Technologie Clé au Service de l’Humanité. RFID: a Key Technology for Humanity,” Comptes Rendus Physique, vol. 19, iss. 1-2, pp. 64-71, Feb. 2018.
V. Kulyukin, C. Gharpure, J. Nicholson and G. Osborne. “Robot-assisted wayfinding for the visually impaired in structured indoor environments.” Auton. Robots, 21(1), pp. 29-41, 2006.
P. Solanki, (2010) “Passive vs active rfid tags.” Internet: https://www.buzzle.com/articles/rfid-technology/.
N.C Wu, M.A. Nystrom, T.R. Lin and Yu, H.C., 2006, July. “Challenges to global RFID adoption.” In Technol. Manag. for the Global Future,Vol. 2, pp. 618-623, 2006.
T. Amemiya, J. Yamashita, K. Hirota and M. Hirose. “Virtual leading blocks for the deaf-blind: A real-time way-finder by verbal-nonverbal hybrid interface and high-density RFID tag space.” In Virtual Reality, Proc., pp. 165-287. Mar. 2004.
M. A. Sáenz Correa, “Sistema de posición y orientación móvil parapersonas ciegas en ambientes cerrados”, M.S. thesis, Depto. Ciencias de la Computación, Univ. de Chile, 2009.
H. Liu, H. Darabi, P. Banerjee and J. Liu. “Survey of wireless indoor positioning techniques and systems.” IEEE Trans. Systems, Man, and Cybern., Part C (Apps and Reviews), 37(6), pp.1067-1080, 2007.
L. Ran, S. Helal and S. Moore. “Drishti: an integrated indoor/outdoor blind navigation system and service.” In Pervasive Computing and Communications, 2004, pp. 23-30. 2004.
N. B. Priyantha, A. Chakraborty and H. Balakrishnan. “The cricket location-support system.” In Proc. MobiCom00, 2000, pp. 32-43.
L. Ran, S. Helal and S. Moore. “Drishti: an integrated indoor/outdoor blind navigation system and service.” In Pervasive Comput. and Commun., 2004, pp. 23-30.
K. Lorincz, and M. Welsh, “A Robust, Decentralized Approach to RF-Based Location Tracking.” Harvard University, Cambridge. MA, Tech. Rep. TR-19-04, 2004.
H. Huang, G. Gartner, M. Schmidt and Y. Li. “Smart environment for ubiquitous indoor navigation.” In Intl. Conf. on New Trends in Inf. and Service Sci., 2009, pp. 176-180.
Z. Zuo, L. Liu, L. Zhang and Y. Fang. “Indoor Positioning Based on Bluetooth Low-Energy Beacons Adopting Graph Optimization.” Sensors, vol. 18, no. 11, pp. 3736, 2018.
Y.J. Chang, S.K. Tsai and T.Y. Wang. “A context aware handheld wayfinding system for individuals with cognitive impairments.” In Proc. 10th Intl. ACM SIGACCESS Conf. Comp. and Access., 2008, pp. 27-34.
M. Bessho S. Kobayashi, N. Koshizuka and K. Sakamura. “A space-identifying ubiquitous infrastructure and its application for tour-guiding service.” In Proc. 2008 ACM Symp. App. Comp., 2008, pp. 1616-1621.
P. Zheng and L. Ni. “Smart phone and next generation mobile computing”, Ed. Elsevier. San Francisco, CA, USA: 2005.
F. Franceschini, M. Galetto, D. Maisano, L. Mastrogiacomo, and B. Pralio, "Large-scale dimensional metrology: the new paradigm of distributed systems", In Distrib, Large-Scale Dimensional Metrology. London, UK: Springer, 2011, pp.1-22
] J. Kang, J. Seo, and Y. Won, "Ephemeral ID beacon-based improved indoor positioning system", Symmetry, vol. 10, no. 11, pp. 622-634, Nov. 2018.
V. Filipe, F. Fernandes, H. Fernandes, A. Sousa, H. Paredes, and J. Barroso. “Blind navigation support system based on Microsoft Kinect.” Procedia Comput. Sci., 14, pp. 94-101, 2012.
J. Baus, A. Krüger and W. Wahlster. “A resource-adaptive mobile navigation system.” In Proc. 7th Intl. Conf. Intel. U. Int., 2002, pp. 15-22.
V. Tsetsos, C. Anagnostopoulos, P. Kikiras and S. Hadjiefthymiades. “Semantically enriched navigation for indoor environments.” Intl. J. Web and Grid Services, vol. 2, no. 4, pp.453-478, 2006.
A.R. Golding and N. Lesh. “Indoor navigation using a diverse set of cheap, wearable sensors.” In Wearable Comput., The Third Intl. Symp., 1999, pp. 29-36.
A. Hub, J. Diepstraten and T. Ertl. “Design and development of an indoor navigation and object identification system for the blind.” In ACM Sigaccess Access. and Comput., no. 77-78, pp. 147-152, Oct. 2004.
J. Rajamäki, P. Viinikainen, J. Tuomisto, T. Sederholm and M. Säämänen. “LaureaPOP indoor navigation service for the visually impaired in a WLAN environment.” In Proc. 6th WSEAS Intl. Conf. Electron., Hardware, Wireless and Opt. Commun., 2007, pp. 96-101.
G. Retscher and M. Thienelt. “NAVIO–a navigation and guidance service for pedestrians.” Positioning, vol. 3, no. 1-2, pp. 208-217, 2004.
J. Hightower and G. Borriello. “Location systems for ubiquitous computing.” Comput., vol. 34, no. 8, pp. 57-66, 2001.
M.A. Williams, A. Hurst, and S.K. Kane. "Pray before you step out" describing personal and situational blind navigation behaviors.” In Proc. 15th Intl. ACM SIGACCESS Conf. Comput. and Access., pp. 1-8, 2013.
L.A.,.Guerrero, F. Vasquez, and S. F. Ochoa. "An indoor navigation system for the visually impaired." Sensors vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 8236-8258, 2012.
R. Ivanov, “Indoor navigation system for visually impaired”, in Proc. 11th Intl. Conf. on Comput. Syst. and Technol. and Workshop for PhD Students in Comput., Sofia, Bulgaria, 2010, pp. 143-149.
J.M. Benjamin and N.A. Ali, 1974, March. “An improved laser cane for the blind”, in Proc. Quantitative Imagery in the Biomed. Sci. II ,Vol. 40, San Diego, USA, 1974, pp. 101-105.
Q. K. Dang, Y. Chee, D. D. Pham, and Y. S. Suh. “A virtual blind cane using a line laser-based vision system and an inertial measurement unit.” Sensors, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 95, 2016.
L. Kay. “A sonar aid to enhance spatial perception of the blind: engineering design and evaluation.” Radio and Electron. Eng., vol. 44, no. 11, pp.605-627, 1974.
K. Ito, M. Okamoto, J. Akita, T.Ono, I. Gyobu, T. Takagi, T. Hoshi and Y. Mishima. “CyARM: an alternative aid device for blind persons.” In CHI'05 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Comput. Syst., pp. 1483-1488, Apr. 2005.
N. Pressey. “Mowat sensor.” Focus, vol. 11, no. 3, pp.35-39, 1977.
A.G. Dodds. “The sonic pathfinder: An evaluation.” J. of Visual Impairment and Blindness, vol. 78, no. 5, pp.203-206, 1984.
J.A. Brabyn. “New developments in mobility and orientation aids for the blind.” IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., vol. 4, pp.285-289, 1982.
L. Kay. “Electronic aids for blind persons: an interdisciplinary subject.” IEE Proc. A - Phys. Sci., Meas. and Instrum., Manag. and Educ.-Reviews, vol. 131, no. 7, pp. 559-576, 1984.
S. Vorapatratorn, and K. Nambunmee. “iSonar: an obstacle warning device for the totally blind.” J. of Assistive, Rehabilitative & Therapeutic Technol., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 23114, 2014.
C. Khampachua, C. Wongrajit, R. Waranusast, and P. Pattanathaburt. “Wrist-mounted smartphone-based navigation device for visually impaired people using ultrasonic sensing.” In 2016 Fifth ICT Intl. Student Project Conf. (ICT-ISPC) IEEE, pp. 93-96, 2016.
F. Xiao, Q. Miao, X. Xie, L. Sun and R. Wang. “Indoor anti-collision alarm system based on wearable Internet of Things for smart healthcare.” IEEE Commun. Magazine, vol. 56, no. 4, pp.53-59, 2018.
C. P. Chen, J. Zhou,and W. Zhao. “A real-time vehicle navigation algorithm in sensor network environments”. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst., 13(4), pp. 1657-1666, 2012.
S. Storandt, "Algorithms for vehicle navigation", Faculty of Comput. Sci. Elect. Eng. Inform. Technol., Dec. 2012.
E. Apostolopoulos, N. Fallah, E. Folmer and K.E. Bekris. “Feasibility of interactive localization and navigation of people with visual impairments.” In Proc. 11th IEEE IAS-10, pp.22-32, 2010.
Zeng, L., & Weber, G. (2011). “Accessible maps for the visually impaired.” In Proc. IFIP Interact 2011 Workshop on ADDW, pp. 54-60.
O. Koch and S. Teller. “A Self-calibrating, vision-based navigation assistand”, in Workshop on Comput. Vision Appl. for the Visually Impaired, Marseille, Francia, 2008.
J.M. Loomis, R.G. Golledge and R.L. Klatzky. “Navigation system for the blind: Auditory display modes and guidance.” Presence, vol. 7, no. 2, pp.193-203, 1998.
R. Etter and M. Specht. “Melodious walkabout: Implicit navigation with contextualized personal audio contents”, in Proc. Pervasive Comput., pp. 43-49 , 2005.
S. Holland, D.R. Morse and H. “Gedenryd. AudioGPS: Spatial audio navigation with a minimal attention interface.” Personal and Ubiquitous Comput., vol. 6, no. 4, pp.253-259, 2002.
M. Nassih, I. Cherradi, Y. Maghous, B. Ouriaghli and Y. Salih-Alj. “Obstacles recognition system for the blind people using RFID.” In 6th Intl. Conf. NGMAST, 2012, pp. 60-63.
T. Amemiya, J. Yamashita, K. Hirota and M. Hirose. “Virtual leading blocks for the deaf-blind: A real-time way-finder by verbal-nonverbal hybrid interface and high-density RFID tag space.” In Virtual Reality, 2004, pp. 165-287.
W. Heuten, N. Henze, S. Boll and M. Pielot. “Tactile wayfinder: a non-visual support system for wayfinding.” In Proc. 5th Nordic Conf. Human-Comput. Interaction: Building Bridges, pp. 172-181, 2008.
S. Willis and S. Helal. “RFID information grid and wearable computing solution to the problem of wayfinding for the blind user in a campus environment.” In IEEE Intl. Symp. Wearable Comp. (ISWC 05), 2005.
S. Ertan, C. Lee, A. Willets, H. Tan and A. Pentland, 1998, October. “A wearable haptic navigation guidance system.” In Wearable Comput., 1998, pp. 164-165.
H. Petrie, V. Johnson, T. Strothotte, A. Raab, S. Fritz and R. Michel. “MoBIC: Designing a travel aid for blind and elderly people.” The J. of Navig., vol. 49, no. 1, pp.45-52, 1996.
K. Nakamura, Y. Aono and Y. Tadokoro. “A walking navigation system for the blind.” Syst. and Comput. in Japan, vol. 28, no. 13, pp.36-45, 1997.
B. Huang and N. Liu. “Mobile navigation guide for the visually disabled.” Transp. Res. Record: J. of the Transp. Res. Board, vol. 1885, no. 1, pp.28-34, 2004.
M. Arikawa, S.I. Konomi and K. Ohnishi. “NAVITIME: Supporting pedestrian navigation in the real world.” IEEE Pervasive Comput., vol. 6, no. 3, 2007.
M.L. Mekhalfi, F. Melgani, A. Zeggada, F.G. De Natale, M.A.M. Salem and A. Khamis. “Recovering the sight to blind people in indoor environments with smart technologies.” Expert Syst. with Appl., vol. 46, pp.129-138, 2016.
H. Montes, I. Chang, G. Carballeda, J. Muñoz, A. García, R. Vejarano, M. Armada, "MOVIDIS: first steps toward help the mobility of people with visual disability in Panama", in Proc. RoboCity16 Open Conf. on Future Trends in Robot., Madrid, Spain, 2016, pp. 211-218.
G. Carballeda, A. Arcia, R. Pérez, y H. Montes, "Aplicación móvil para el monitoreo de personas con discapacidad visual", in Proc. ATICA 2016, Cuenca, Ecuador, 2016, pp. 93-100.
H. Montes, I. Chang, G. Carballeda, J. Muñoz, A. Garcia, R. Vejarano, and Y. Saez, "Design of a System to Support the Mobility of Visually Impaired People", in Proc. CLAWAR 2018, Panama, 2018, pp. 37-44.
Y. Sáez, J. Muñoz, F. Canto, A. García, and H. Montes, “Assisting Visually Impaired People in the Public Transport System through RF-Communication and Embedded Systems”, Sensors, vol. 19, no. 6, pp. 1282-1295, Mar. 2019. DOI: 10.3390/s19061282, [Online].
H. Montes, I. Chang, G. Carballeda, J. Muñoz, Y. Saez, R. Vejarano, and A. Garcia, "Conceptual design of technological systems for the mobility of visual impairment people in indoor buildings", in Proc. IESTEC 2019, Panama, 2019, pp. 1-6. [Online].
D. H. Yen, “Electronic Travel Aids for the Blind”, Texas School for the Blind and Visually Impaired, Austin, TX, USA, Oct. 11, 1996. [Online]. Available: https://www.tsbvi.edu/orientation-and-mobility-items/1974-electronic-travel-aids-for-the-blind.
S. Maidenbaum, S. Hanassy, S. Abboud, G. Buchs, D. R. Chebat, S. Levy-Tzedek and A. Amedi. “The EyeCane, a new electronic travel aid for the blind: Technology, behavior and swift learning.” Restorative Neurol. and Neurosci., vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 813-824, 2014.
L. Kim, S. Park, S. Lee and S. Ha. “An electronic traveler aid for the blind using multiple range sensors.” IEICE Electron. Express, vol. 6, no. 11, pp. 794-799, 2009.
K. Tandon, T. Pande, M. Adil, G. Dubey and A. Kumar. “A blind navigation system using RFID for indoor environments.” Intl. J. of Comput. Syst., vol. 2, no. 4, pp.115-118, 2015.
B. Ding, H. Yuan, L. Jiang, and X. Zang. “The research on blind navigation system based on RFID.” In Wireless Commun., Network. and Mobile Comput., 2007, pp. 2058-2061.
B. Kuipers, R. Browning, B. Gribble, M. Hewett and E. Remolina. “The spatial semantic hierarchy”. Artificial Intell., 2000.
B. Kuipers. “An intellectual history of the spatial semantic hierarchy.” In Robotics and cognitive approaches to spatial mapping, pp. 243-264. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2007.
J. C. Chen, “Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm.” J. of Formalized Math., vol. 15, no. 9, pp. 237-247, 2003.
M. Bolic, D. Simplot-Ryl and I. Stojmenovic. “RFID systems: research trends and challenges.” John Wiley & Sons, 2010.
V. Chawla and D. S. Ha. “An overview of passive RFID”. IEEE Commun. Magazine, vol. 45, no. 9, pp. 11-17, 2007.
O. Bashan. “ISO14443 an Introduction to the contactless standard for smart cards and its relevance to customers”. On Track Innovations, ltd (OTI). Report. 2001.
P. Roux. “The ISO/IEC 14443 cards standard.” In Proc. of 6th International Conference on Automatic Fare Collection-new Horizons in Public Transport with Smart Cards, Bologna, Italy, 2002.
D. Kou, K. Zhao, Y. Tao and W. Kou. “RFID technologies and applications”. In Enabling Technol. for Wireless E-business, pp. 89-108, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2006.
Finkenzeller, K. RFID handbook: Fundamentals and applications in contactless smart cards, radio frequency identification and near-field communication. John Wiley & Sons, 2010. Available: Google books.
D. Paret and R. Riesco. “RFID and contactless smart card applications”, pp. 91-93, New York: Wiley, 2005.
Kimaldi Electronics, [En línea]. Tecnología RFID activa. Available: https://www.kimaldi.com/blog/tecnologia_rfid_activa/.
J. Nievergelt. “Exhaustive search, combinatorial optimization and enumeration: Exploring the potential of raw computing power.” In Intl. Conf. on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Comput. Sci., pp. 18-35, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2000.
R. M. Karp. “On the computational complexity of combinatorial problems”. Networks, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 45-68, 1975.
B. Golden. “Shortest-path algorithms: A comparison”. Oper. Res., vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 1164-1168, 1976.