Electric Field Distribution and Leakage Currents in Glass Insulator Under Different Altitudes and Pollutions Conditions using FEM Simulations
Keywords:
altitude, comsol, electric field, fem, glass insulator, leakage current, pollution, potential distributionAbstract
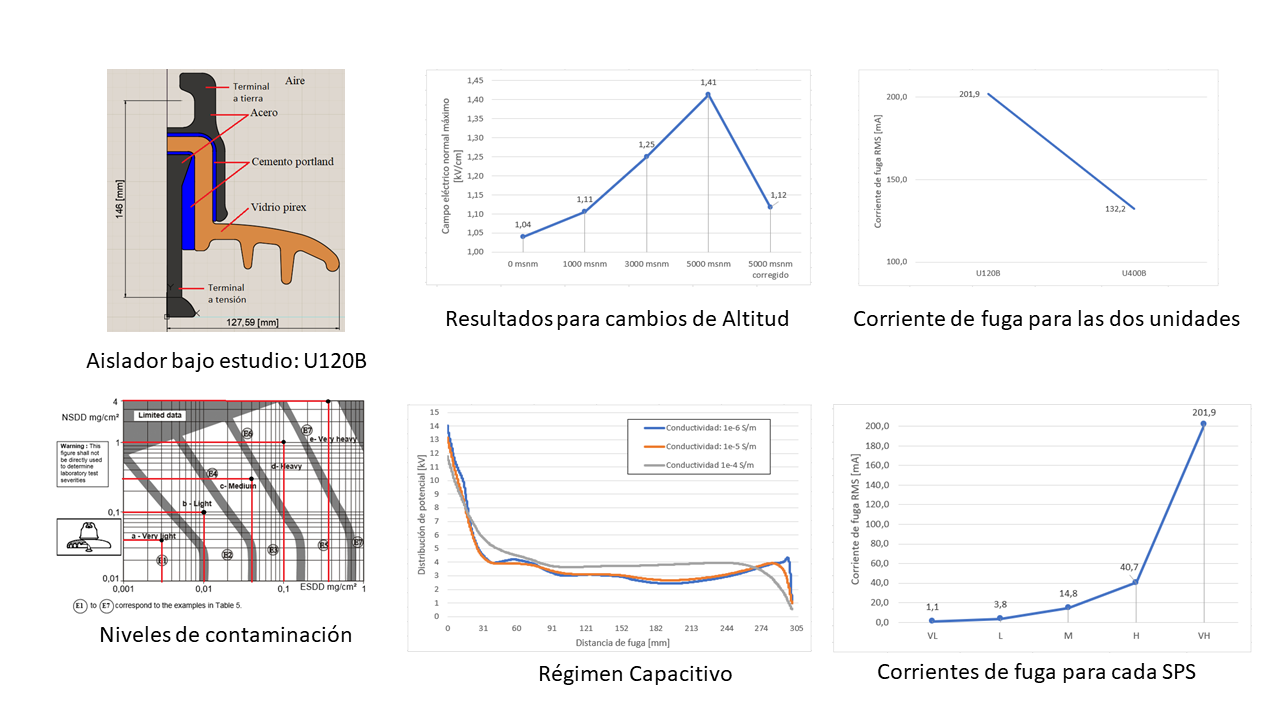
The influence of pollution and atmospheric altitude on the dielectric performance of a glass insulator was studied by means of finite element analysis simulations. Contamination levels were represented by thin layers with different values of conductivities and thicknesses. Altitudes differences were simulated by equivalent voltages using correction factors. The results showed that by increasing the conductivity and altitude values, there was a considerable increase in the concentration of the electric field and leakage currents, changing from capacitive to resistive regime of electrical potential distribution along the insulator surface. The proposed levels of contamination and altitudes were analyzed by increasing the dimensions of the insulator according to IEC standards. In the case of the capacitive regime (conductivities lower than 10-4 S/m) there was a decrease in the electric field intensity up to 21% compared to an insulator at sea level. In resistive regime, a decrease up to 34.5% was obtained for leakage currents considering conductivities calculated according to the site pollution severity shown in the IEC standard. Despite the decrease of the leakage current after the increase of the insulator dimensions based on the standards, it did not mitigate all theoretical leakage current calculated along the insulator surface. Future work will focus on experimental research to validate this theoretical results.
Downloads
References
IEC60071-2, Insulation co-ordination - Part 2: Application guide, International Electrotechnical Commission, 1996.
IEC60815-2, Selection and dimensioning of high-voltage insulators for polluted conditions - Part 2: Ceramic and glass insulators for a.c. systems, International Electrotechnical Commission, 2002.
IEC60815-1, Selection and dimensioning of high-voltage insulators intended for use in polluted conditions - Part 1: Definitions, information and general principles, International Electrotechnical Commission, 2008.
IEC60507, Artificial pollution tests on high-votalge ceramic and glass insulators to be used on a.c. systems, BSI Standards Limited, 2014.
S. F. Stefenon, J. P. Américo, R. B. Grebogi y A. Nied, "Analysis of the Electric Field in Porcelain Pin-Type Insulators via Finite Elements Software," IEEE Latin America Transactions, vol. 16, no 10, pp. 2505-2512, 2018.
A. Arshad, G. Scott y F. Masoud, "Effect of pollution layer conductivity and thickness on electric field distribution along a polymeric insulator," 2015. [En línea]. Available: https://www.comsol.com/paper/download/289991/arshad_paper.pdf [Último acceso: 26 6 2019].
A. S. Krzma, M. Y. Khamaira y M. Abdulsamad, "Comparative Analysis of Electric Field and Potential Distributions over Porcelain and Glass Insulators Using Finite Element Method," Proceedings of the First Conference for Engineering Sciences and Technology, vol. 1, pp. 176-184, 2018.
M. M. Khademi, A. Arjomand y H. Saedpanah, "Dynamic Calculation of Leakage Current and Electric Field of Distribution Polymeric Insulator Under Pollution Layer," The 20th Iranian Electrical Power distribution Conference, pp. 28-29, April 2015.
M. I. Mousa, Z. Abdul-Malek y I. M. Zainab, "Leakage Current Based Thermal Modeling of Glass Disc Insulator Surface," Indonesian Jurnal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 6, no 3, pp. 504-512, 2017.
Arshad, A. Nekahi, S. G. McMeekin y M. Farzaneh, "Numerical Computation of Electric Field and Potential Along Silicone Rubber Insulators Under Contaminated and Dry Band Conditions," 3D Research Center, vol. 7, no 25, 2016.
C. Volat, "Comparison Between the Use of Surface and Volume Conductivity to Compute Potential Distribution along an Insulator in Presence of a Thin Conductive Layer," IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference, pp. 409-413, 2-5 June 2013.
H. P. Mercure, "Insulator Pollution Performance at High Altitude: Major Trends," IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, vol. 4, no 2, pp. 1461-1468, 1989.
R. Sundararajan y R. W. Nowlin, "Effect of Altitude on the Flashover Voltage of Contaminated Insulators," Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, pp. 433-436, 1996.
WG-D1.44, Guidelines for Altitude Correction of Pollution Performance of Insulators, CIGRE, 2017.
E. Asenjo, N. Morales y A. Valdenegro, "Solution of Low Frequency Complex Fields in Polluted Insulators by Means of the Finite Element Method," IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, vol. 4, no 1, pp. 10-16, 1997.
IEC60305, Insulators for overhead lines with a nominal voltage above 1000V - Ceramic or glass insulator units fot a.c. systems - Characteristics of insulator units of cap and pin type, 4 ed., International Electrotechnical Commission, 1995.
E. Seran, M. Godefroy, E. Pili, N. Michielsen y S. Bondiguel, "What we can learn from measurements of air electric conductivity in 222Rn-rich atmosphere," Earth and space science, american geophysical union, vol. 4, no 2, pp. 91-106, 2017.
R. A. Serway, Principles of Physics, 2 ed., Saunders College Pub., 1998.
D. J. McGraw, "The measurement of the dielectric constant of three different shapes of concrete blocks," IJRRAS, vol. 25, no 3, pp. 82-102, 2015.
J. Golubovskaya, "The Physics Factbook," Glenn Elert,, 2004. [En línea]. Available: https://hypertextbook.com/facts/2004/JaneGolubovskaya.shtml [Último acceso: 25 6 2019].
J. Wardman y T. Wilson, "Volcanic Ash Contamination: Limitations of the Standard ESDD Method for Classifying Pollution Severity," IEEE Transactions on Dielectric and Electrical Insulation, vol. 20, no 2, pp. 414-420, 2013.
S. Aquil y D. Schmitt, "Dielectric permittivity of clay obsorbed water: Effect of salinity," 2010. [En línea]. Available: https://geoconvention.com/wp-content/uploads/abstracts/2010/0623_GC2010_Dielectric_permittivity_of_clay_adsorbed_water.pdf [Último acceso: 26 06 2019].
R. Arias, "Insulation failure caused by special pollution around industrial," Engineering Failure Analysis, vol. 102, pp. 126-135, 2019.
WG-C4.303, Outdoor Insulation in Polluted Conditions: Guidelines for Selection and Dimensioning, Part 1: General principles and the AC case, CIGRE, 2008.
R. Arias y J. Mejia, "The need of creating a new nominal creepage distance in accordance with heaviest pollution 500 kV overhead line insulators," Engineering Failure Analysis, vol. 86, pp. 21-32, 2018.