Ranking Model Applying Self-Organizing Maps and Factor Analysis
Keywords:
Factor Analysis , Ranking Model, Self-Organizing MapsAbstract
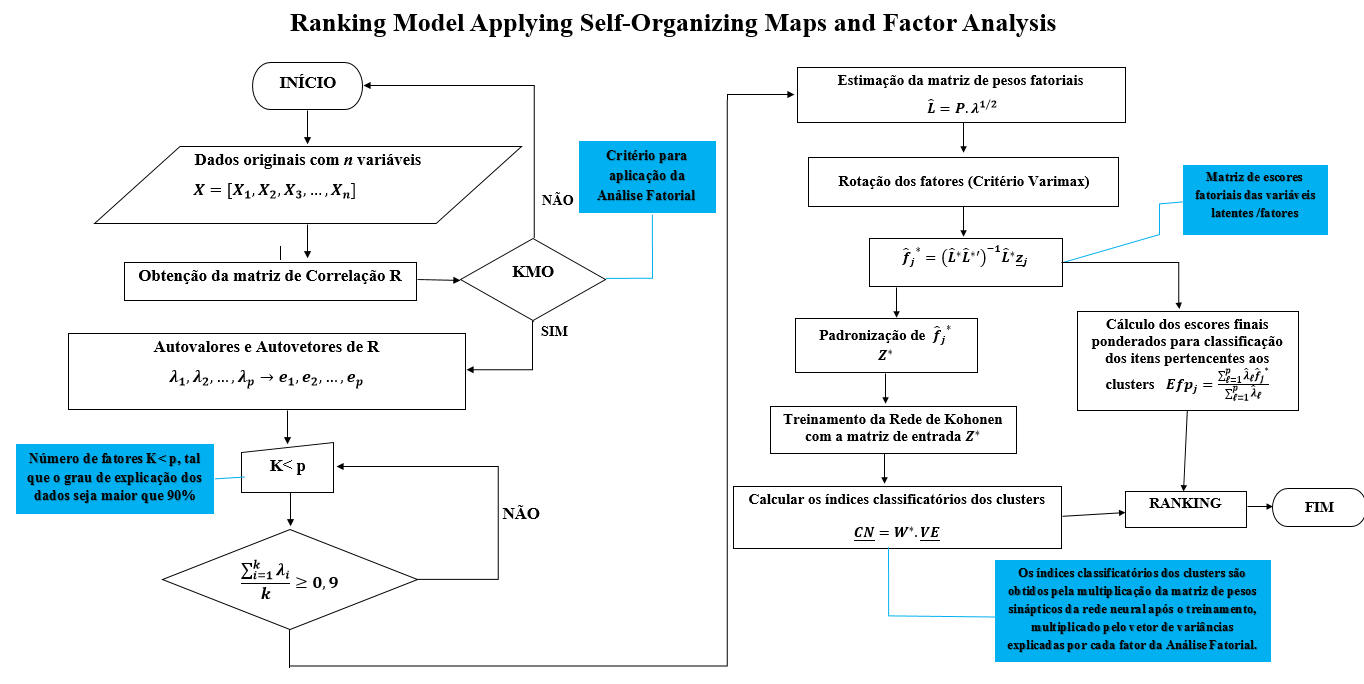
The present work aims to use Self-Organizing Maps (SOM) to group ranking results obtained by factor analysis. In this paper we propose the application of Factor Analysis at a stage prior to the application of the SOM, in order to use the factor scores of latent variables as input data for network training, as these scores carry practically all information regarding the variables of the lattice problem, losing only an insignificant portion of variability. Thus, the resulting map will present the cluster according to the efficiency shown in the Factor Analysis. The application refers to the performance evaluation of 50 employees of a company by means of scores on four psychological assessment tests (exams) and three indicators of sales results. The result of ranking these vendors according to performance was grouped into four homogeneous clusters.
Downloads
References
R. Esquarcini and J. M. Marques. “Classificação dos municípios paranaenses Segundo suas políticas setoriaispela análise multivariada.” Revista da FAE, v.9, p. 83-93, 2006.
E. M. Furtado, A. Chaves Neto and Z. H. Domingues. “Ranqueamento de faxinais do estado do Paraná através da Análise Fatorial”. Revista Ciências exatas e Naturais – RECEN. Unicentro, v.5, n.1, 2003.
Q. Ma, W. Wang, Q. Yao, J. Zhou e L. Quo. “Factor analysis on call detail record.” In Proceedings of the 2018 27 th Wireless and Opyical Communication Conference (WOCC 2018), Hualien, Taiwan, pp. 1-5, 30 April-1 May 2018.
M. Cottrell and M. Verleysen. “Advances in Self-Organizing Maps.” Neural Networks 19, p. 721-722, 2006.
L. Churilov and A. Flitman. “Towards fair ranking of Olympics achievements: the case of Sidney 2000.” Computers & Operational Research, v.33, p. 2057-2082, 2004.
C. Spearman. “General intelligence objectively determined and measured.” American Journal of Psychology, v.15, p.201-293, 1904.
L. L. Thurstone. “The vector of mind.” Chicago: University of Chicago, 1935.
A. S. Kaplunovsky. “Why using factor analysis? dedicated to the centenary of factor analysis. 2009.” [Online]. Available: http://www.magniel.com/fa/kaplunovky.pdf. Accessed on: Nov. 5, 2019.
F. H. C. Marriot. “The interpretation of multiple observations.” New York, Academic Press, 117 p., 1974.
L. S. Kubrusly. “O Modelo de Análise Fatorial. Dissertação de Mestrado. UFRJ, 1981.
J. F. Hair, R. E. Anderson, R. L. Tathan and W. C. Black. “Multivariate Data Analysis.” 6 th ed. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Ed. 2006.
R. A. Johnson and D. W. Wichern. “Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis.” 6 th ed. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Ed. 2007.
J. Maroco. “Análise Estatística com utilização do SPSS.” 3 rd ed. Lisboa: Edições Sílabo. 822 p., 2007.
L. V. Fauset. “Fundamentals of Neural Networks: Architectures, Algorithms, and Aplications”. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Ed. p.246-287, 1994.
A. Ultch and C. Vetter. “Self-Organizing Feature Maps versus Statistical Clustering Methods: A Benchmark.” Research Report No. 9, Dep. Of Mathematics, University of Marburg, 1994.
T. Kohonen. “Self-Organizing formation of topologically correct feature maps.” Biological Cybernetics, v. 43, p. 59-69, 1982.
H. Simon. “Neural Networks – A Comprehensive foundation.” 2 nd ed. Canadá: Prentice Hall, Ed., 1999.
L. O. L. Oliveira. “Mapas Auto-Organizáveis de Kohonen aplicados ao mapeamento de ambientes de robótica móvel.” Dissertação de mestrado, Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, 2001.
Y. Kou, H. Cui and L. Xu. “The Application of SOM and K-Means Algorithms in Public Security Performance Analysis and Forecasting.” In: Khachidze V., Wang T., Siddiqui S., Liu V., Cappuccio S., Lim A. (eds) Contemporary Research on E-business Technology and Strategy. iCETS 2012. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 332. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34447-3_7
L. Zinger. A. Gobet and T. Pommier. “Two decades of describing the unseen majority of aquatic microbial diversity.” Mol Ecol. Apr;21(8):1878-96. Doi:10.1111/j.1365294X.2011.05362.x. 2012