Proposal for a Methodology Based on Electricity Consumption to Analyze Social Isolation During a COVID-19 Pandemic: Case Study
Keywords:
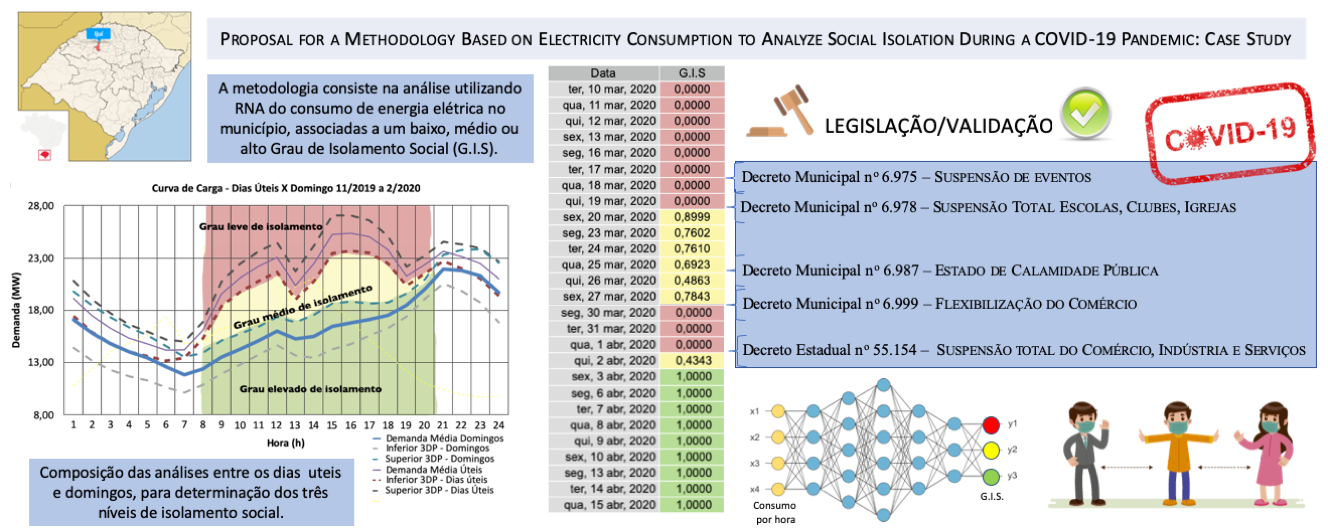
COVID-19, social insolation, energy demand, Artificial Neural NetworkAbstract
The first occurrences of Covid-19 disease caused by the coronavirus SRA-CoV-2, appeared in the region of Wuhan (China) expanding rapidly around the world. Based on this, the World Health Organization characterized this situation as a pandemic. The solution adopted by the health authorities was to apply social isolation. Thus, one of the challenges is the correct dimensioning and quantification of compliance with these measures. This paper presents a new methodology to evaluate the social isolation, considering the consumption of electric energy of the population of a medium-sized city, located in the northwest of the state of Rio Grande do Sul (RS), Brazil. The methodology consists of the combination of a data set on electricity consumption in the municipality, in which energy consumption ranges are associated with a low, medium or high degree of social isolation. An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is trained to evaluate the degree of social isolation practiced by the its population. The data to validate the performance of the proposed methodology are generated from real data provided by the municipality's energy utility. From the simulations results the ANN immediately identified the level of social isolation practiced by the people of the city using only the information on the population's electricity consumption.
Downloads