Dynamic dispatch algorithm proposal for last-mile delivery vehicle
Keywords:
Last-mile delivery, schedulingAbstract
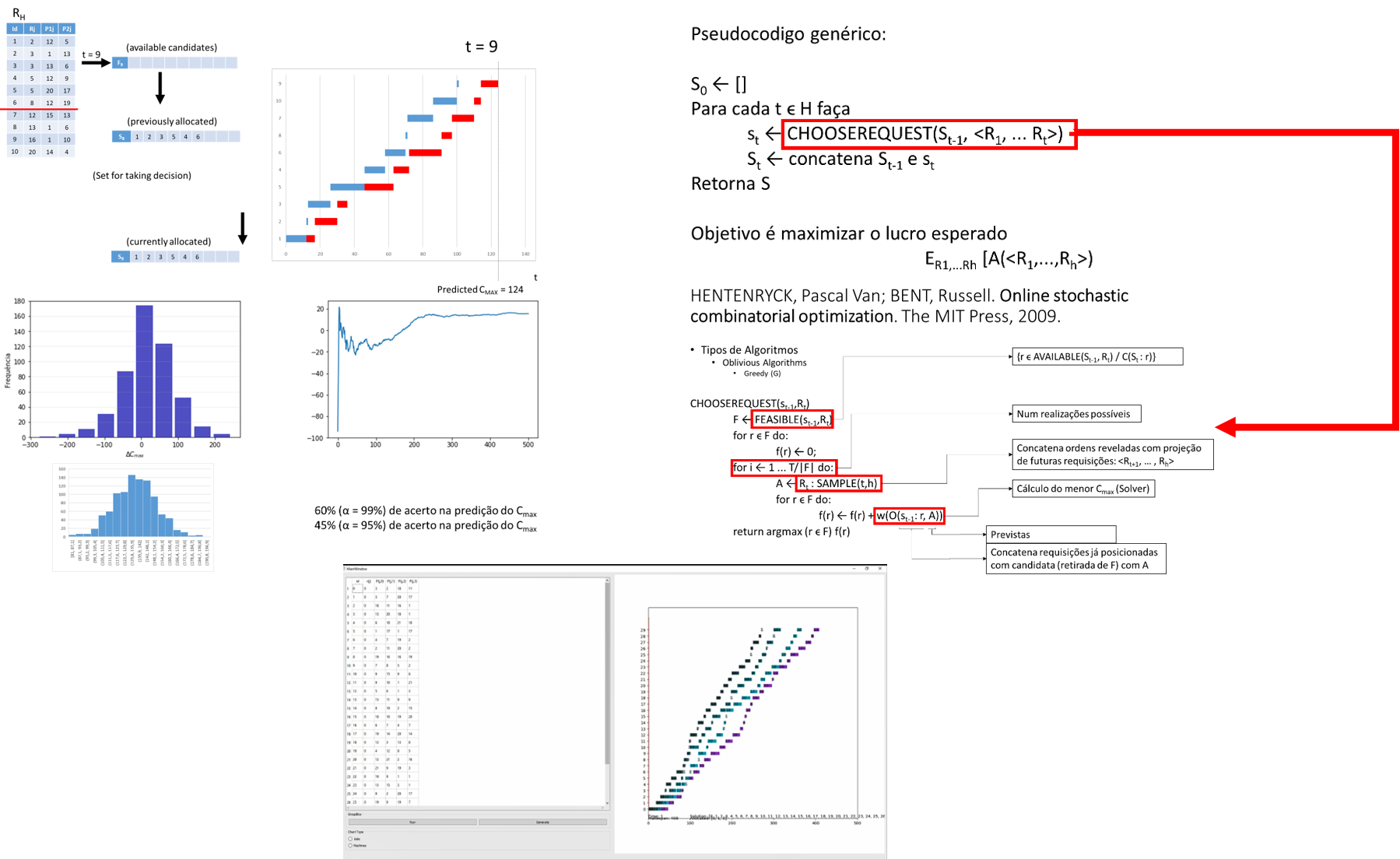
The complex urban scenario demands decisions which needs to be taken not only fast, but considering a high level of uncertainty. In such context, this study proposes an algorithm to address the vehicle allocation scheduling with a request list unknown a priori, and is revealed along the operation horizon. Based on the OSCO (online stochastic combinatorial optimization) problem, it is presented a framework to operate such problem in a last-mile delivery system where customers’ requests from e-commerce (or food delivery) along an operations day. The deterministic calculation was realized using a permutational flowshop scheduling problem with the objective of minimizing makespan. Experiments indicated convergence in the algorithm along the planning trials, and a satisfactory makespan prediction, before the orders are revealed, with accuracy. The probability distribution adheres with a bell-shaped (normal) distribution with its population parameters estimated using classical statistics inference theory. Incorporating uncertain in such type of mathematical modeling could open doors for a new era of systems in current days with cloud computing, big data, smart cities, and artificial intelligence.
Downloads