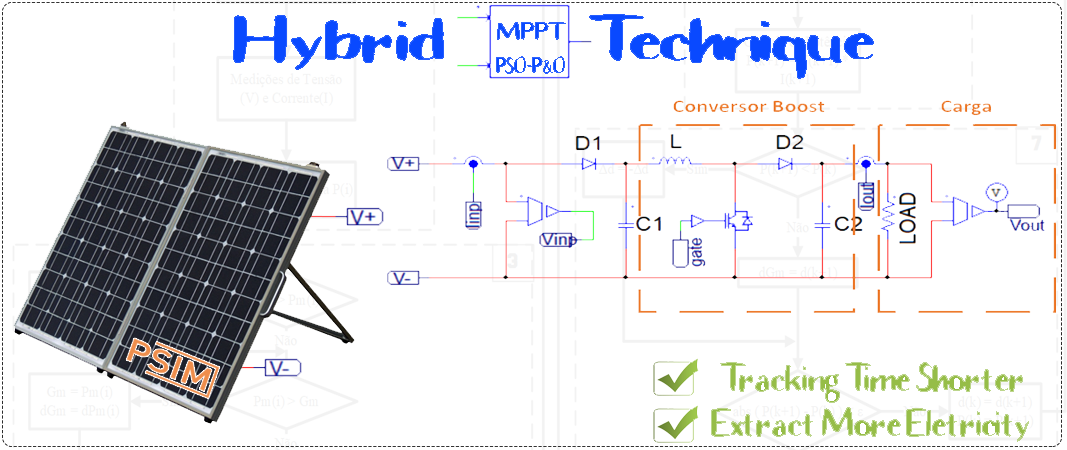
Hybrid MPPT Technique PSO-P&O Applied to Photovoltaic Systems Under Uniform and Partial Shading Conditions
Keywords:
Maximum Power Point Tracking, Particle Swarm Optimization, Perturb & ObserveAbstract
The PV array must always operate at the Global Maximum Power Point (GMPP) in order to make the most of the energy generated. In this context, some classical techniques achieve this goal satisfactorily under uniform shading conditions. However, environmental conditions vary during the day and these methods fail to extract the highest power available under partial shading conditions. The present paper aims to propose a hybrid Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) technique that uses Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Perturb & Observe (P&O) methods, applied to photovoltaic systems under uniform and partial shading conditions. The photovoltaic system was modeled in the PSIM software. The proposed MPPT technique is compared with the classical P&O, standard PSO and a hybrid P&O-PSO techniques. The simulation results showed that the proposed hybrid algorithm can track GMPP under uniform and partial shading conditions and tracking time is 50% shorter than standard PSO technique. Furthermore, the proposed method manages to extract 0.3% more electricity from the photovoltaic system compared to the P&O-PSO hybrid
Downloads
References
IEA. “World Energy Outlook 2018,” International Energy Agency. Paris, France. 2018.
EPE (Empresa de Pesquisa Energética). “Balanço Energético Nacional 2019: Ano Base 2018,”. Rio de Janeiro, Maio de 2019.
Femia, Nicola, et al. “Power electronics and control techniques for maximum energy harvesting in photovoltaic systems,” CRC press, 2017.
Batzelis, Efstratios I., Pavlos S. Georgilakis, and Stavros A. Papathanassiou. “Energy models for photovoltaic systems under partial shading conditions: a comprehensive review.” IET Renewable Power Generation 9.4 (2014): 340-349.
Kobayashi, Kenji, Ichiro Takano, and Yoshio Sawada. “A study on a two stage maximum power point tracking control of a photovoltaic system under partially shaded insolation conditions.” 2003 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting. Vol. 4. IEEE, 2003.
Rezk, Hegazy, and Ali M. Eltamaly. “A comprehensive comparison of different MPPT techniques for photovoltaic systems.” Solar energy 112 (2015): 1-11.
Safari, Azadeh, and Saad Mekhilef. “Simulation and hardware implementation of incremental conductance MPPT with direct control method using cuk converter.” IEEE transactions on industrial electronics 58.4 (2010): 1154-1161.
Xiao, Weidong, and William G. Dunford. “A modified adaptive hill climbing MPPT method for photovoltaic power systems.” 2004 IEEE 35th annual power electronics specialists conference (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37551). Vol. 3. Ieee, 2004.
Alajmi, Bader N., et al. “A maximum power point tracking technique for partially shaded photovoltaic systems in microgrids.” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 60.4 (2011): 1596-1606.
Tajuddin, Mohammad Faridun Naim, et al. “Evolutionary based maximum power point tracking technique using differential evolution algorithm.” Energy and Buildings 67 (2013): 245-252.
Eberhart, Russell, and James Kennedy. “A new optimizer using particle swarm theory.” MHS'95. Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science. Ieee, 1995.
Yang, Bo, et al. “Novel bio-inspired memetic salp swarm algorithm and application to MPPT for PV systems considering partial shading condition.” Journal of cleaner production 215 (2019): 1203-1222.
Miyatake, Masafumi, et al. “Maximum power point tracking of multiple photovoltaic arrays: A PSO approach.” IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems 47.1 (2011): 367-380.
Liu, Yi-Hwa, et al. “A particle swarm optimization-based maximum power point tracking algorithm for PV systems operating under partially shaded conditions.” IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 27.4 (2012): 1027-1035.
Renaudineau, Hugues, et al. “A PSO-based global MPPT technique for distributed PV power generation.” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 62.2 (2014): 1047-1058.
Ishaque, Kashif, and Zainal Salam. “A deterministic particle swarm optimization maximum power point tracker for photovoltaic system under partial shading condition.” IEEE transactions on industrial electronics 60.8 (2012): 3195-3206.
Lian, K. L., J. H. Jhang, and I. S. Tian. “A maximum power point tracking method based on perturb-and-observe combined with particle swarm optimization.” IEEE journal of photovoltaics 4.2 (2014): 626-633.
Manickam, Chakkarapani, et al. “A hybrid algorithm for tracking of GMPP based on P&O and PSO with reduced power oscillation in string inverters.” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 63.10 (2016): 6097-6106.
Patel, Hiren, and Vivek Agarwal. “MATLAB-based modeling to study the effects of partial shading on PV array characteristics.” IEEE transactions on energy conversion 23.1 (2008): 302-310.
Carotenuto, Pietro Luigi, et al. “About the criteria for triggering the reconfiguration of a photovoltaic array.” 2014 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE). IEEE, 2014.