Wind Turbine Emulator: A Tool for Experimental and Computational Study
Keywords:
Control system, Hardware-in-the-loop, Wind turbine emulator, Wind utilizationAbstract
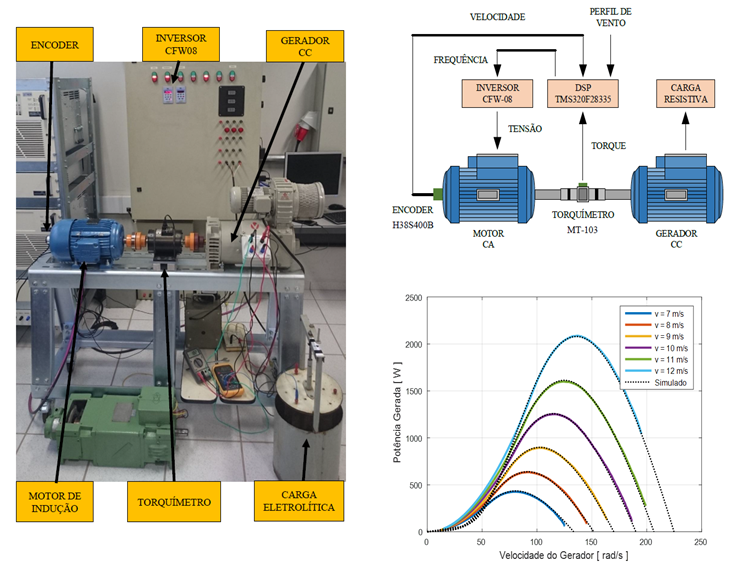
Renewable sources of energy appear to be a great solution to problems related to rising demand for electricity and the ever-growing worldwide concern about carbon dioxide emission levels as they are non-polluting, clean and abundant. Wind energy is one of the most promising forms of renewable energy. Thus, in order to further improve wind generation technology, this work presents a wind turbine emulator (WTE) capable of simulating power curves of a turbine by means of hardware-in-the-loop control. An WTE is an important tool for the development of renewable energy systems providing a controllable test environment that allows the evaluation and improvement of control schemes which is difficult to acquire in real wind turbines as wind speed is random. Thus, this paper presents the analysis, modeling and experimental implementation of a wind turbine emulator using a three-phase induction motor (TIM) driven by a frequency inverter. For this, a closed loop control of torque and speed is implemented. This control causes the TIM along with the frequency inverter to emulate the actual behavior of a wind turbine, considering variations in wind dynamics, aerodynamic phenomena, load effects and pitch angle. The control algorithm is designed via MATLAB / Simulink® software and communication between the computational model and the experimental bench is ensured through the microcontroller DSP TMS320F28335. Using a torque sensor and an encoder, this model defines the torque level on the system shaft and the rotational speed of the TIM. These signals are fed back to the computational model and thus the power curve of the WTE is defined with the voltage level to be applied to the frequency inverter. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of using the TIM-frequency inverter assembly for emulating a wind turbine, since the WTE can represent a real wind turbine.
Downloads